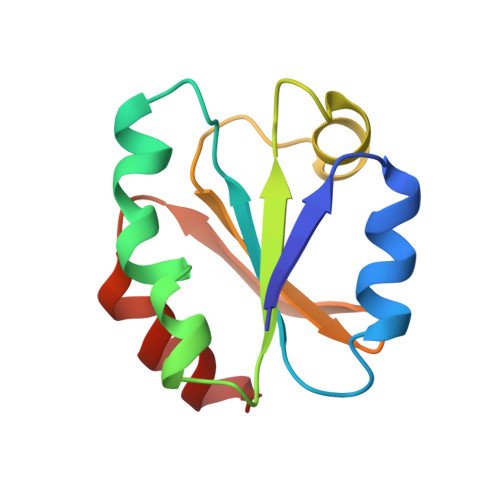
Solution structure of human thioredoxin in a mixed disulfide intermediate complex with its target peptide from the transcription factor NF kappa B.
Qin, J., Clore, G.M., Kennedy, W.M., Huth, J.R., Gronenborn, A.M.(1995) Structure 3: 289-297
- PubMed: 7788295
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00159-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MDI, 1MDJ, 1MDK - PubMed Abstract:
Human thioredoxin is a 12 kDa cellular redox protein that plays a key role in maintaining the redox environment of the cell. It has recently been shown to be responsible for activating the DNA-binding properties of the cellular transcription factor, NF kappa B, by reducing a disulfide bond involving Cys62 of the p50 subunit. Using multidimensional heteronuclear-edited and hetero-nuclear-filtered NMR spectroscopy, we have solved the solution structure of a complex of human thioredoxin and a 13-residue peptide extending from residues 56-68 of p50, representing a kinetically stable mixed disulfide intermediate along the reaction pathway. The NF kappa B peptide is located in a long boot-shaped cleft on the surface of human thioredoxin delineated by the active-site loop, helices alpha 2, alpha 3 and alpha 4, and strands beta 3 and beta 4. The peptide adopts a crescent-like conformation with a smooth 110 degrees bend centered around residue 60 which permits it to follow the path of the cleft. In addition to the intermolecular disulfide bridge between Cys32 of human thioredoxin and Cys62 of the peptide, the complex is stabilized by numerous hydrogen-bonding, electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions which involve residues 57-65 of the NF kappa B peptide and confer substrate specificity. These structural features permit one to suggest the specificity requirements for human thioredoxin-catalyzed disulfide bond reduction of proteins.
- Laboratory of Chemical Physics, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892-0520, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: