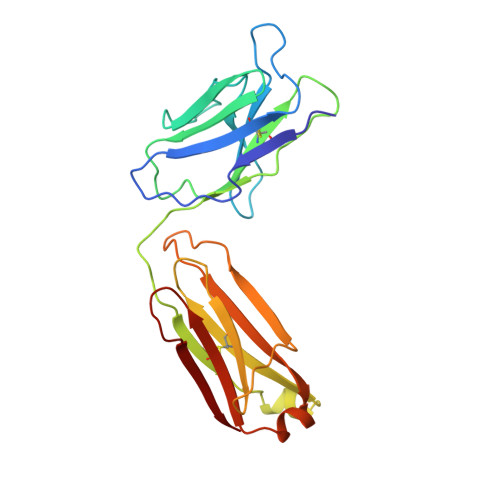
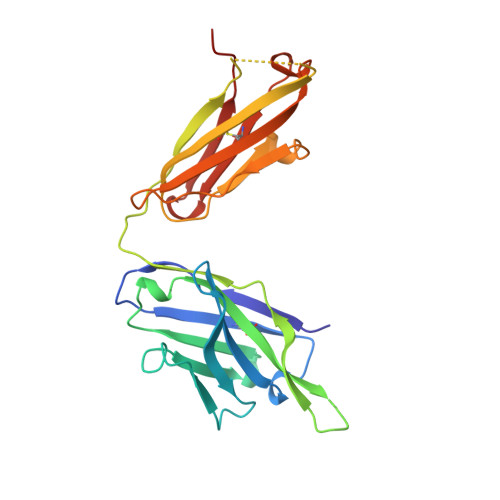
Three-dimensional structure of an Fab-peptide complex: structural basis of HIV-1 protease inhibition by a monoclonal antibody.
Lescar, J., Stouracova, R., Riottot, M.M., Chitarra, V., Brynda, J., Fabry, M., Horejsi, M., Sedlacek, J., Bentley, G.A.(1997) J Mol Biology 267: 1207-1222
- PubMed: 9150407
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.0950
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MF2, 2HRP - PubMed Abstract:
F11.2.32, a monoclonal antibody raised against HIV-1 protease (Kd = 5 nM), which inhibits proteolytic activity of the enzyme (K(inh) = 35(+/-3)nM), has been studied by crystallographic methods. The three-dimensional structure of the complex between the Fab fragment and a synthetic peptide, spanning residues 36 to 46 of the protease, has been determined at 2.2 A resolution, and that of the Fab in the free state has been determined at 2.6 A resolution. The refined model of the complex reveals ten well-ordered residues of the peptide (P36 to P45) bound in a hydrophobic cavity at the centre of the antigen-binding site. The peptide adopts a beta hairpin-like structure in which residues P38 to P42 form a type II beta-turn conformation. An intermolecular antiparallel beta-sheet is formed between the peptide and the CDR3-H loop of the antibody; additional polar interactions occur between main-chain atoms of the peptide and hydroxyl groups from tyrosine residues protruding from CDR1-L and CDR3-H. Three water molecules, located at the antigen-antibody interface, mediate polar interactions between the peptide and the most buried hypervariable loops, CDR3-L and CDR1-H. A comparison between the free and complexed Fab fragments shows that significant conformational changes occur in the long hypervariable regions, CDR1-L and CDR3-H, upon binding the peptide. The conformation of the bound peptide, which shows no overall structural similarity to the corresponding segment in HIV-1 protease, suggests that F11.2.32 might inhibit proteolysis by distorting the native structure of the enzyme.
- Unité d'Immunologie Structurale (URA 1961 CNRS), Département d'Immunologie, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France.
Organizational Affiliation: