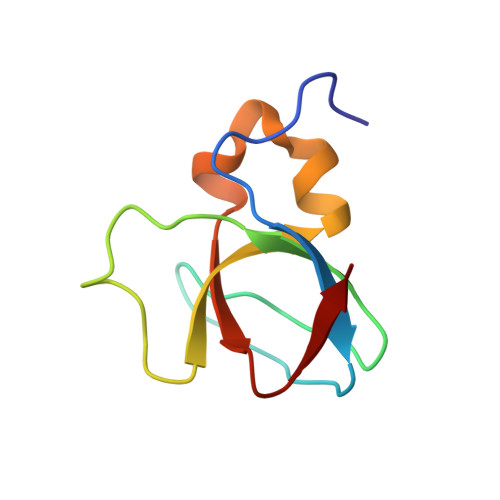
A structure-based model of the c-Myc/Bin1 protein interaction shows alternative splicing of Bin1 and c-Myc phosphorylation are key binding determinants.
Pineda-Lucena, A., Ho, C.S., Mao, D.Y., Sheng, Y., Laister, R.C., Muhandiram, R., Lu, Y., Seet, B.T., Katz, S., Szyperski, T., Penn, L.Z., Arrowsmith, C.H.(2005) J Mol Biology 351: 182-194
- PubMed: 15992821
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.05.046
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MUZ, 1MV0, 1MV3 - PubMed Abstract:
The N terminus of the c-Myc oncoprotein interacts with Bin1, a ubiquitously expressed nucleocytoplasmic protein with features of a tumor suppressor. The c-Myc/Bin1 interaction is dependent on the highly conserved Myc Box 1 (MB1) sequence of c-Myc. The c-Myc/Bin1 interaction has potential regulatory significance as c-Myc-mediated transformation and apoptosis can be modulated by the expression of Bin1. Multiple splicing of the Bin1 transcript results in ubiquitous, tissue-specific and tumor-specific populations of Bin1 proteins in vivo. We report on the structural features of the interaction between c-Myc and Bin1, and describe two mechanisms by which the binding of different Bin1 isoforms to c-Myc may be regulated in cells. Our findings identify a consensus class II SH3-binding motif in c-Myc and the C-terminal SH3 domain of Bin1 as the primary structure determinants of their interaction. We present biochemical and structural evidence that tumor-specific isoforms of Bin1 are precluded from interaction with c-Myc through an intramolecular polyproline-SH3 domain interaction that inhibits the Bin1 SH3 domain from binding to c-Myc. Furthermore, c-Myc/Bin1 interaction can be inhibited by phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62, a functionally important residue found within the c-Myc SH3-binding motif. Our data provide a structure-based model of the c-Myc/Bin1 interaction and suggest a mode of regulation that may be important for c-Myc function as a regulator of gene transcription.
- Ontario Cancer Institute and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, 610 University Avenue, Toronto, Ont., Canada M5G 2M9.
Organizational Affiliation: