Mechanisms of Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe inhibition of thrombin.
Hasan, A.A., Warnock, M., Nieman, M., Srikanth, S., Mahdi, F., Krishnan, R., Tulinsky, A., Schmaier, A.H.(2003) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285: H183-H193
- PubMed: 12598231
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00490.2002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NY2 - PubMed Abstract:
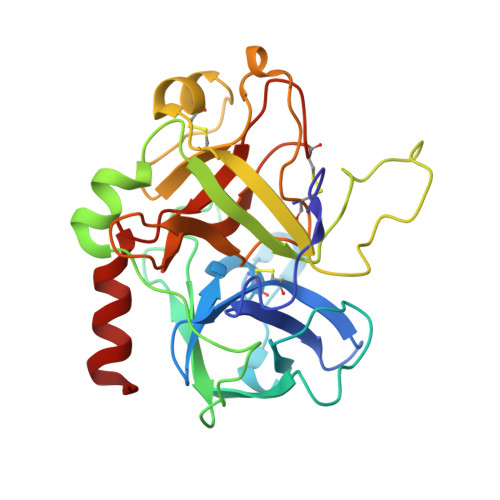
Investigations determined the mechanism(s) by which Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe (RPPGF) inhibits thrombin-induced platelet activation. High concentrations of RPPGF inhibit thrombin-induced coagulant activity. RPPGF binds to the active site of thrombin by forming a parallel beta-strand with Ser214-Gly216 and interacts with His57, Asp189, and Ser195 of the catalytic triad. RPPGF competitively inhibits alpha-thrombin from hydrolyzing Sar-Pro-Arg-paranitroanilide with a Ki = 1.75 +/- 0.03 mM. Other mechanisms were sought to explain why RPPGF inhibits thrombin activation of platelets at concentrations below that which inhibits its active site. Soluble RPPGF blocks biotinylated NATLDPRSFLLR of the thrombin cleavage site on protease-activated receptor (PAR)1 from binding to the peptide RPPGC (IC50 = 20 microM). The soluble recombinant extracellular domain of PAR1 (rPAR1EC) blocks biotinylated RPPGF binding to rPAR1EC (IC50 = 50 microM) bound to microtiter plates, but rPAR1EC deletion mutants missing the sequence LDPR or PRSF do not. RPPGF and related forms prevent the thrombin-like enzyme thrombocytin from proteolyzing rPAR1EC at concentrations that do not block thrombocytin's active site. These studies indicate that RPPGF is a bifunctional inhibitor of thrombin: it binds to PAR1 to prevent thrombin cleavage at Arg41 and interacts with the active site of alpha-thrombin.
- Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI 48109-0640, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: