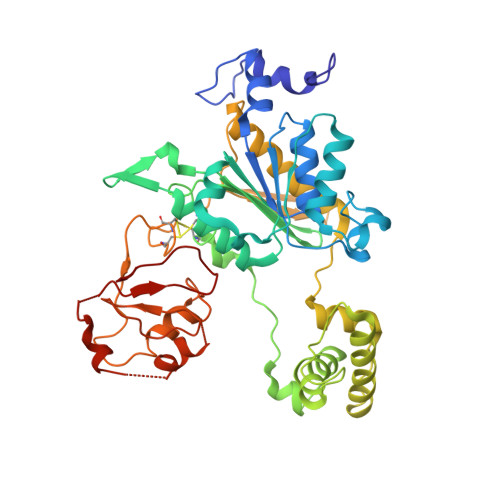
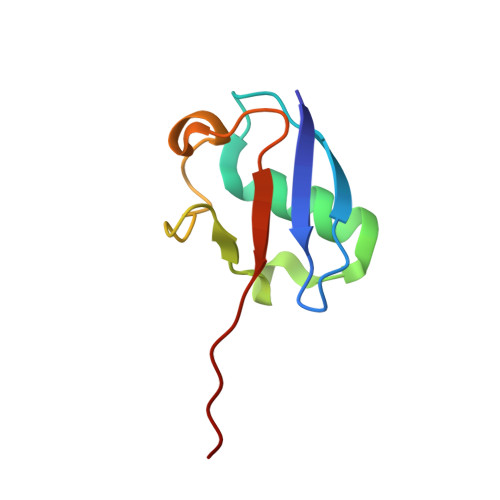
The structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP complex reveals the basis for selective ubiquitin-like protein activation by an E1.
Walden, H., Podgorski, M.S., Huang, D.T., Miller, D.W., Howard, R.J., Minor, D.L., Holton, J.M., Schulman, B.A.(2003) Mol Cell 12: 1427-1437
- PubMed: 14690597
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00452-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1R4M, 1R4N - PubMed Abstract:
E1 enzymes initiate ubiquitin-like protein (ubl) transfer cascades by catalyzing adenylation of the ubl's C terminus. An E1's selectivity for its cognate ubl is essential because the E1 subsequently coordinates the ubl with its correct downstream pathway. We report here the structure of the 120 kDa quaternary complex between human APPBP1-UBA3, a heterodimeric E1, its ubl NEDD8, and ATP. The E1 selectively recruits NEDD8 through a bipartite interface, involving a domain common to all ubl activating enzymes including bacterial ancestors, and also eukaryotic E1-specific sequences. By modeling ubiquitin into the NEDD8 binding site and performing mutational analysis, we identify a single conserved arginine in APPBP1-UBA3 that acts as a selectivity gate, preventing misactivation of ubiquitin by NEDD8's E1. NEDD8 residues that interact with E1 correspond to residues in ubiquitin important for binding the proteasome and other ubiquitin-interacting proteins, suggesting that the conjugation and recognition machineries have coevolved for each specific ubl.
- Departments of Structural Biology and Genetics/Tumor Cell Biology, St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN 38105, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: