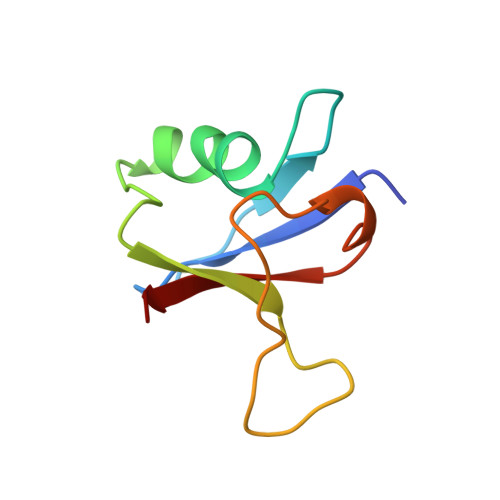
Solution structure of the Ras-binding domain of c-Raf-1 and identification of its Ras interaction surface.
Emerson, S.D., Madison, V.S., Palermo, R.E., Waugh, D.S., Scheffler, J.E., Tsao, K.L., Kiefer, S.E., Liu, S.P., Fry, D.C.(1995) Biochemistry 34: 6911-6918
- PubMed: 7766599
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00021a001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RFA - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the Ras-binding domain of human c-Raf-1 (residues 55-132) has been determined in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Following complete assignment of the backbone and side-chain 1H, 15N, and 13C resonances, the structure was calculated using the program CHARMM. Over 1300 NOE-derived constraints were applied, resulting in a detailed structure. The fold of Raf55-132 consists of a five-stranded beta-sheet, a 12-residue alpha-helix, and an additional one-turn helix. It is similar to those of ubiquitin and the IgG-binding domain of protein G, although the three proteins share very little sequence identity. The surface of Raf55-132 that interacts with Ras has been identified by monitoring perturbation of line widths and chemical shifts of 15N-labeled Raf55-132 resonances during titration with unlabeled Ras-GMPPNP. The Ras-binding site is contained within a spatially contiguous patch comprised of the N-terminal beta-hairpin and the C-terminal end of the alpha-helix.
- Roche Research Center, Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Nutley, New Jersey 07110, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: