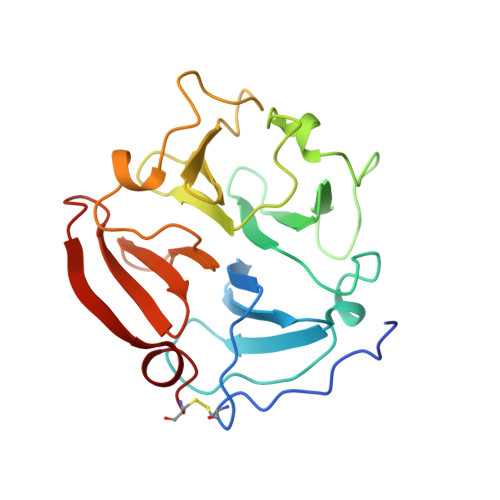
The C-terminal (haemopexin-like) domain structure of human gelatinase A (MMP2): structural implications for its function.
Gohlke, U., Gomis-Ruth, F.X., Crabbe, T., Murphy, G., Docherty, A.J., Bode, W.(1996) FEBS Lett 378: 126-130
- PubMed: 8549817
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)01435-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RTG - PubMed Abstract:
In common with most other matrix metalloproteinases, gelatinase A has a non-catalytic C-terminal domain that displays sequence homology to haemopexin. Crystals of this domain were used by molecular replacement to solve its molecular structure at 2.6 A resolution, which was refined to an R value of 17.9%. This structure has a disc-like shape, with the chain folded into a beta-propeller structure that has pseudo four-fold symmetry. Although the topology and the side-chain arrangement are very similar to the equivalent domain of fibroblast collagenase, significant differences in surface charge and contouring are observable on 1 side of the gelatinase A disc. This difference might be a factor in allowing the gelatinase A C-terminal domain to bind to natural inhibitor TIMP-2.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, Abteilung für Strukturforschung, Martinsried bei München, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: