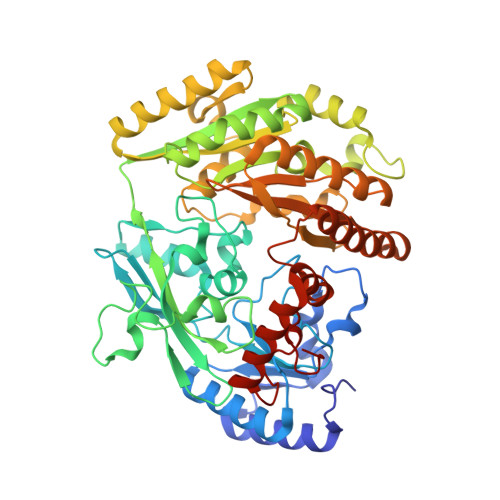
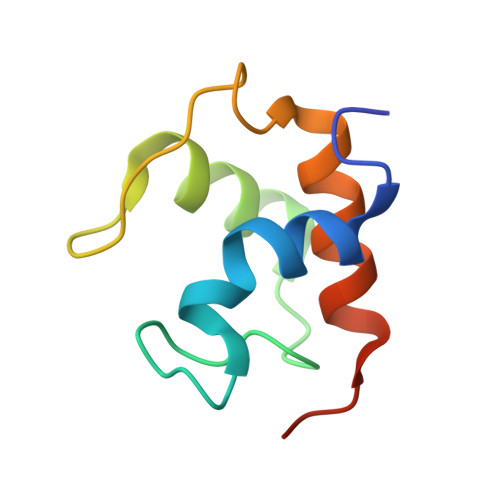
p-Cresol Methylhydroxylase: Alteration of the Structure of the Flavoprotein Subunit upon Its Binding to the Cytochrome Subunit
Cunane, L.M., Chen, Z.-W., McIntire, W.S., Mathews, F.S.(2005) Biochemistry 44: 2963-2973
- PubMed: 15723539
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi048020r
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WVE, 1WVF - PubMed Abstract:
The structures of two forms of a recombinant flavoprotein have been determined at high resolution and compared. These proteins are (1) the flavocytochrome c p-cresol methylhydroxylase (rPCMH, 1.85 A resolution) and (2) the cytochrome-free flavoprotein subunit of rPCMH (PchF, 1.30 A resolution). A significant conformational difference is observed in a protein segment that is in contact with the re face of the isoalloxazine ring of FAD when the structure of PchF is compared to the subunit in the intact flavocytochrome. This structural change is important for optimum catalytic function of the flavoprotein, which has been shown to be dependent on the presence of the cytochrome subunit. This change results in different protein-flavin and apparently different protein-substrate interactions that have a "tuning effect" on the electronic and redox properties of bound p-cresol and the covalently bound FAD. The conformational change in the segment in the cofactor-binding site is induced by a small rearrangement in the flavoprotein-cytochrome interface region of the flavoprotein.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri 63110, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: