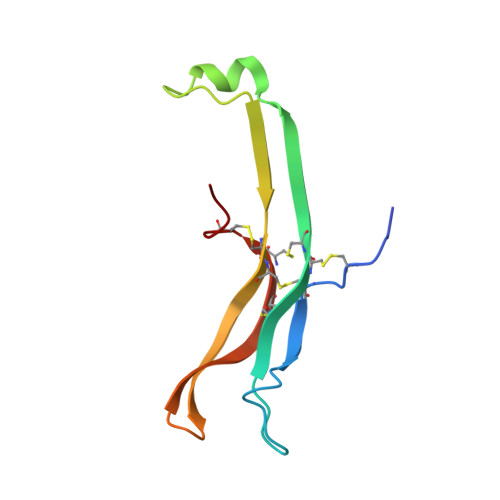
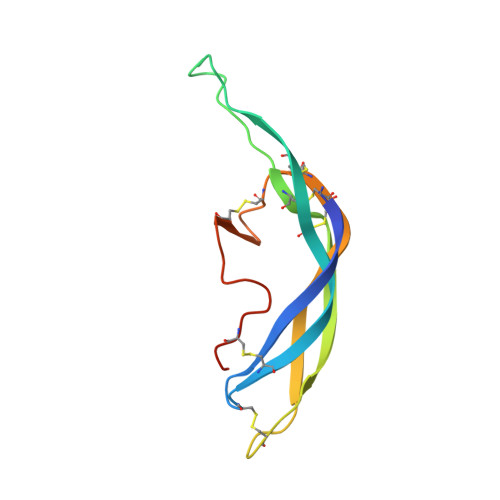
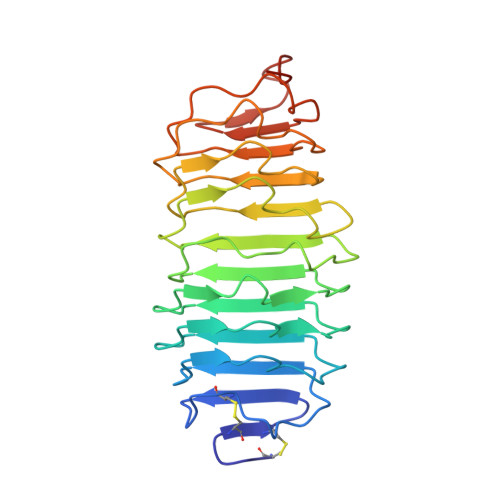
Structure of human follicle-stimulating hormone in complex with its receptor.
Fan, Q.R., Hendrickson, W.A.(2005) Nature 433: 269-277
- PubMed: 15662415
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03206
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XWD - PubMed Abstract:
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is central to reproduction in mammals. It acts through a G-protein-coupled receptor on the surface of target cells to stimulate testicular and ovarian functions. We present here the 2.9-A-resolution structure of a partially deglycosylated complex of human FSH bound to the extracellular hormone-binding domain of its receptor (FSHR(HB)). The hormone is bound in a hand-clasp fashion to an elongated, curved receptor. The buried interface of the complex is large (2,600 A2) and has a high charge density. Our analysis suggests that all glycoprotein hormones bind to their receptors in this mode and that binding specificity is mediated by key interaction sites involving both the common alpha- and hormone-specific beta-subunits. On binding, FSH undergoes a concerted conformational change that affects protruding loops implicated in receptor activation. The FSH-FSHR(HB) complexes form dimers in the crystal and at high concentrations in solution. Such dimers may participate in transmembrane signal transduction.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, New York 10032, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: