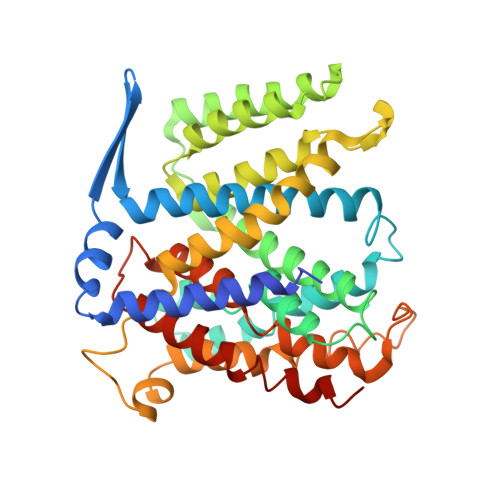
Structure of a Na+/H+ antiporter and insights into mechanism of action and regulation by pH.
Hunte, C., Screpanti, E., Venturi, M., Rimon, A., Padan, E., Michel, H.(2005) Nature 435: 1197-1202
- PubMed: 15988517
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03692
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZCD - PubMed Abstract:
The control by Na+/H+ antiporters of sodium/proton concentration and cell volume is crucial for the viability of all cells. Adaptation to high salinity and/or extreme pH in plants and bacteria or in human heart muscles requires the action of Na+/H+ antiporters. Their activity is tightly controlled by pH. Here we present the crystal structure of pH-downregulated NhaA, the main antiporter of Escherichia coli and many enterobacteria. A negatively charged ion funnel opens to the cytoplasm and ends in the middle of the membrane at the putative ion-binding site. There, a unique assembly of two pairs of short helices connected by crossed, extended chains creates a balanced electrostatic environment. We propose that the binding of charged substrates causes an electric imbalance, inducing movements, that permit a rapid alternating-access mechanism. This ion-exchange machinery is regulated by a conformational change elicited by a pH signal perceived at the entry to the cytoplasmic funnel.
- Department of Molecular Membrane Biology, Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, Max-von-Laue-Str. 3, D-60438 Frankfurt, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: