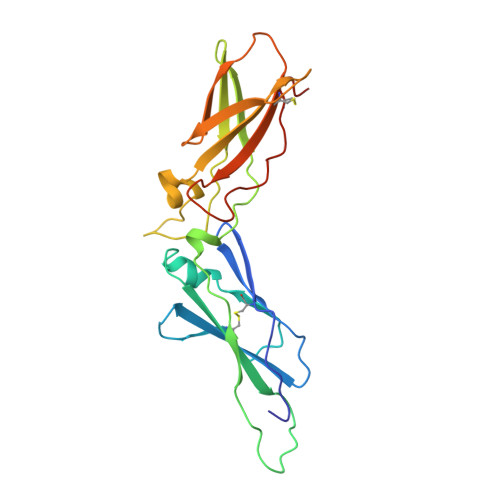
Crystal structure of the extracellular region of human tissue factor.
Harlos, K., Martin, D.M., O'Brien, D.P., Jones, E.Y., Stuart, D.I., Polikarpov, I., Miller, A., Tuddenham, E.G., Boys, C.W.(1994) Nature 370: 662-666
- PubMed: 8065454
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/370662a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BOY - PubMed Abstract:
Tissue factor is a cell-surface glycoprotein receptor which initiates the blood coagulation cascade after vessel injury by interacting with blood clotting factor VII/VIIa and which is implicated in various pathological processes. When bound to tissue factor, factor VII is readily converted to the active protease factor VIIa by trace amounts of factors Xa, IXa or VIIa. Human tissue factor consists of 263 residues, the first 219 of which comprise the extracellular region. We have determined the crystal structure of the extracellular region at a resolution of 2.2 A. Tissue factor consists of two immunoglobulin-like domains associated through an extensive, novel, interdomain interface region. The binding site for factor VII lies at the interface region and involves residues from domain 1 and an extended loop (binding 'finger') of domain 2. This is the first reported structure of a representative of the class 2 cytokine receptor family, which also includes interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma (refs 2, 3) and interleukin-10 (ref. 4) receptors.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, Oxford Centre for Molecular Sciences, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: