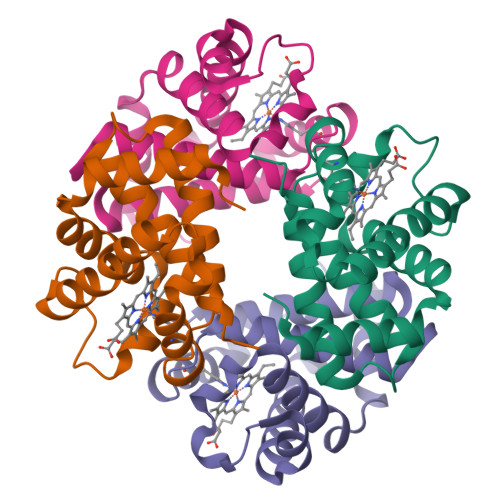
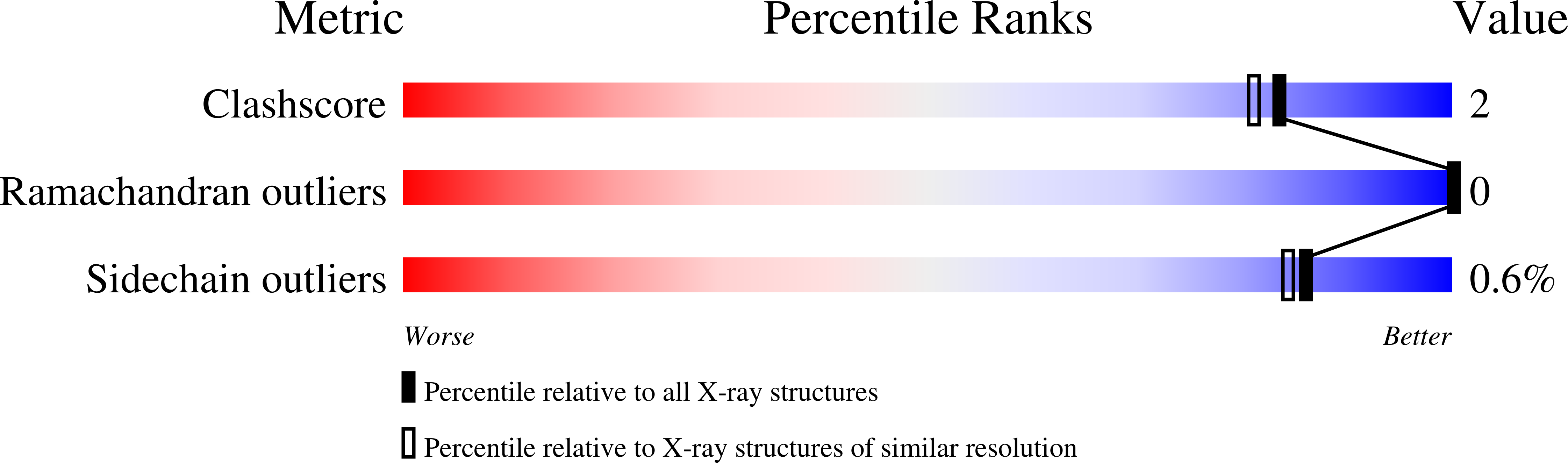Minimal structural requirements for root effect: crystal structure of the cathodic hemoglobin isolated from the antarctic fish Trematomus newnesi
Mazzarella, L., Bonomi, G., Lubrano, M.C., Merlino, A., Riccio, A., Vergara, A., Vitagliano, L., Verde, C., di Prisco, G.(2006) Proteins 62: 316-321
- PubMed: 16299734
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.20709
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AA1 - PubMed Abstract:
The cathodic hemoglobin component of the Antarctic fish Trematomus newnesi (HbCTn) is a Root-effect protein. The interpretation of its functional properties in relation to its sequence is puzzling. Indeed, HbCTn sequence is characterized by an extremely low histidyl content, and in particular by the lack of His146beta and His69beta, which are believed to be important in Bohr and Root effects, respectively. Furthermore, previous analyses suggested that the local environment of Asp95alpha, Asp99beta, and Asp101beta should not be appropriate for the formation of Asp-Asp interactions, which are important for the Root effect. Here, we report the high-resolution crystal structure of the deoxy form of HbCTn. Our data provide a structural interpretation for the very low oxygen affinity of the protein and insights into the structural determinants of the Root effect protein. The structure demonstrates that the presence of Ile41alpha and Ser97alpha at the alpha1beta2 interface does not prevent the formation of the inter-Asp interactions in HbCTn, as previous studies had suggested. The present data indicate that the hydrogen bond formed between Asp95alpha and Asp101beta, which is stabilized by Asp99beta, is per se sufficient to generate the Root effect, and it is the minimal structural requirement needed for the design of Root-effect Hbs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Dipartimento di Chimica, Universitá degli Studi di Napoli Federico II, Naples, Italy. mazzarella@chemistry.unina.it