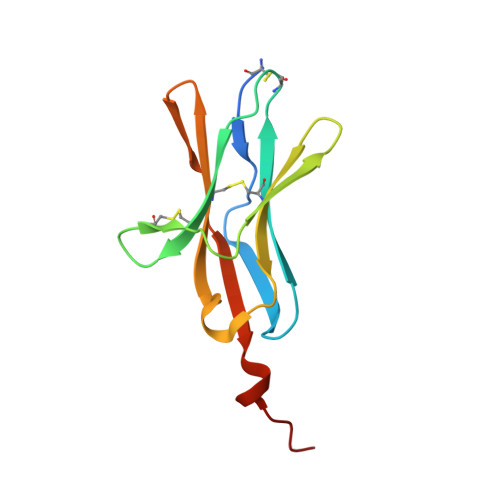
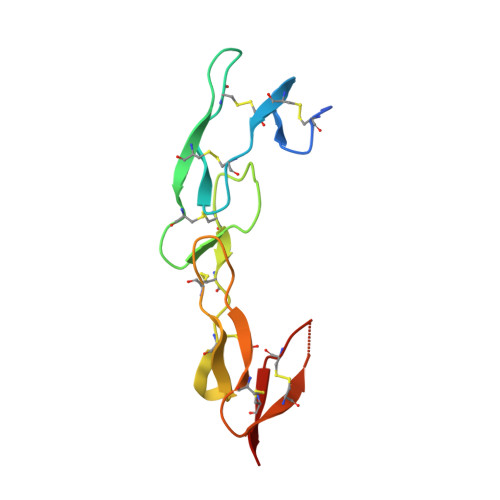
Attenuating Lymphocyte Activity: the crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex
Compaan, D.M., Gonzalez, L.C., Tom, I., Loyet, K.M., Eaton, D., Hymowitz, S.G.(2005) J Biological Chem 280: 39553-39561
- PubMed: 16169851
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507629200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AW2 - PubMed Abstract:
Five CD28-like proteins exert positive or negative effects on immune cells. Only four of these five receptors interact with members of the B7 family. The exception is BTLA (B and T lymphocyte attenuator), which instead interacts with the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member HVEM (herpes virus entry mediator). To better understand this interaction, we determined the 2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex. This structure shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface compared with other CD28-like receptors. Moreover, the structure shows that BTLA recognizes the same surface on HVEM as gD (herpes virus glycoprotein D) and utilizes a similar binding motif. Light scattering analysis demonstrates that the extracellular domain of BTLA is monomeric and that BTLA and HVEM form a 1:1 complex. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis of HVEM was used to further define critical binding residues. Finally, BTLA adopts an immunoglobulin I-set fold. Despite structural similarities to other CD28-like members, BTLA represents a unique co-receptor.
- Department of Protein Engineering, Genentech, Inc., S. San Francisco, California 94080, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: