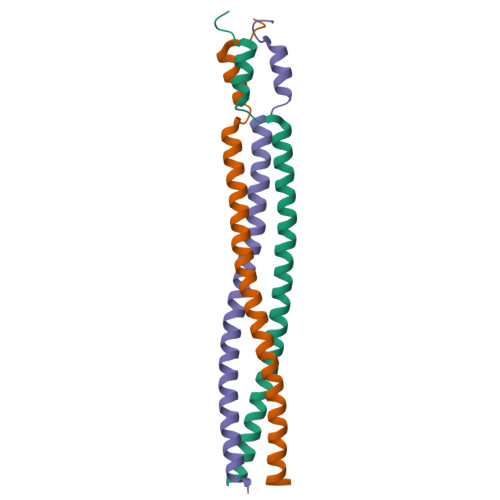
Crystal structure of the DUF16 domain of MPN010 from Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Shin, D.H., Kim, J.-S., Yokota, H., Kim, R., Kim, S.-H.(2006) Protein Sci 15: 921-928
- PubMed: 16522803
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.051993506
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BA2 - PubMed Abstract:
We have determined the crystal structure of the DUF16 domain of unknown function encoded by the gene MPN010 of Mycoplasma pneumoniae at 1.8 A resolution. The crystal structure revealed that this domain is composed of two separated homotrimeric coiled-coils. The shorter one consists of 11 highly conserved residues. The sequence comprises noncanonical heptad repeats that induce a right-handed coiled-coil structure. The longer one is composed of approximately nine heptad repeats. In this coiled-coil structure, there are three distinguishable regions that confer unique structural properties compared with other known homotrimeric coiled-coils. The first part, containing one stutter, is an unusual phenylalanine-rich region that is not found in any other coiled-coil structures. The second part is a highly conserved glutamine-rich region, frequently found in other trimeric coiled-coil structures. The last part is composed of prototype heptad repeats. The phylogenetic analysis of the DUF16 family together with a secondary structure prediction shows that the DUF16 family can be classified into five subclasses according to N-terminal sequences. Based on the structural comparison with other coiled-coil structures, a probable molecular function of the DUF16 family is discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
College of Pharmacy, Ewha Womans Unversity, Seoul 120-750, Korea.