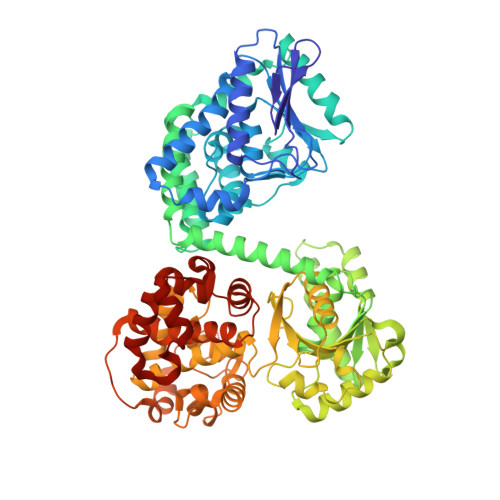
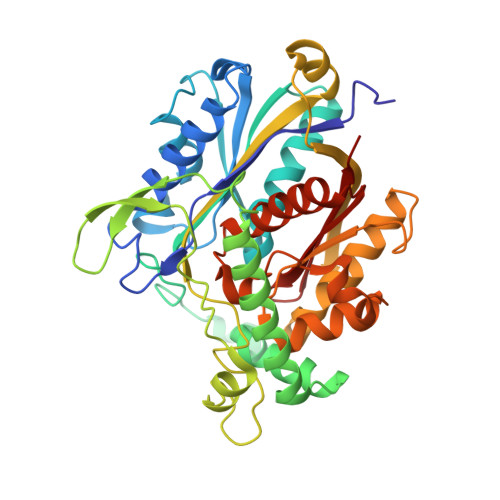
Ligand-Induced Domain Rearrangement of Fatty Acid beta-Oxidation Multienzyme Complex
Tsuchiya, D., Shimizu, N., Ishikawa, M., Suzuki, Y., Morikawa, K.(2006) Structure 14: 237-246
- PubMed: 16472743
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2005.10.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D3T - PubMed Abstract:
The quaternary structure of a fatty acid beta-oxidation multienzyme complex, catalyzing three sequential reactions, was investigated by X-ray crystallographic and small-angle X-ray solution scattering analyses. X-ray crystallography revealed an intermediate structure of the complex among the previously reported structures. However, the theoretical scattering curves calculated from the crystal structures remarkably disagree with the experimental profiles. Instead, an ensemble of the atomic models, which were all calculated by rigid-body optimization, reasonably explained the experimental data. These structures significantly differ from those in the crystals, but they maintain the substrate binding pocket at the domain boundary. Comparisons among these structures indicated that binding of 3-hydroxyhexadecanoyl-CoA or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide induces domain rearrangements in the complex. The conformational changes suggest the structural events occurring during the chain reaction catalyzed by the multienzyme complex.
- Biomolecular Engineering Research Institute, 6-2-3 Furuedai, Suita, Osaka 565-0874, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: