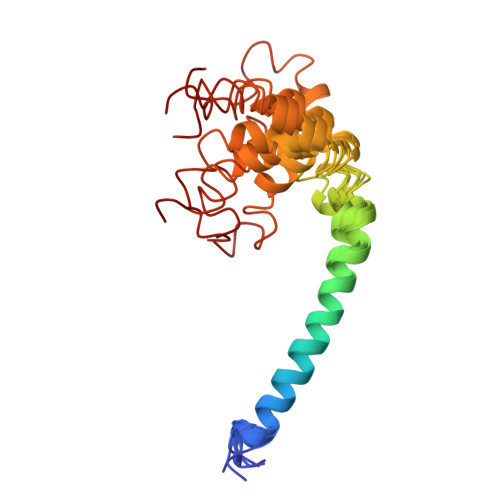
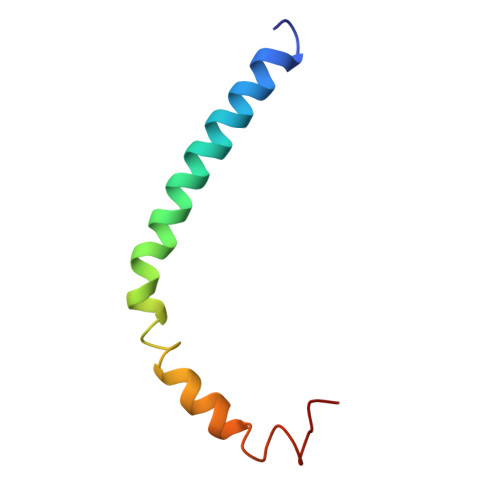
The three-dimensional structure of CsmA: A small antenna protein from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum.
Pedersen, M.O., Underhaug, J., Dittmer, J., Miller, M., Nielsen, N.C.(2008) FEBS Lett 582: 2869-2874
- PubMed: 18652828
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.07.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2K37 - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of the chlorosome baseplate protein CsmA from Chlorobium tepidum in a 1:1 chloroform:methanol solution was determined using liquid-state NMR spectroscopy. The data reveal that the 59-residue protein is predominantly alpha-helical with a long helical domain extending from residues V6 to L36, containing a putative bacteriochlorophyll a binding domain, and a short helix in the C-terminal part extending from residues M41 to G49. These elements are compatible with a model of CsmA having the long N-terminal alpha-helical stretch immersed into the lipid monolayer confining the chlorosome and the short C-terminal helix protruding outwards, thus available for interaction with the Fenna-Matthews-Olson antenna protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Insoluble Protein Structures (inSPIN), Interdisciplinary Nanoscience Center (iNANO) and Department of Chemistry, University of Aarhus, Langelandsgade 140, Aarhus C, Denmark.