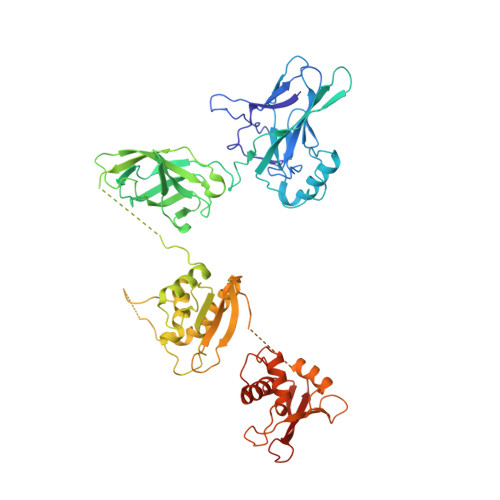
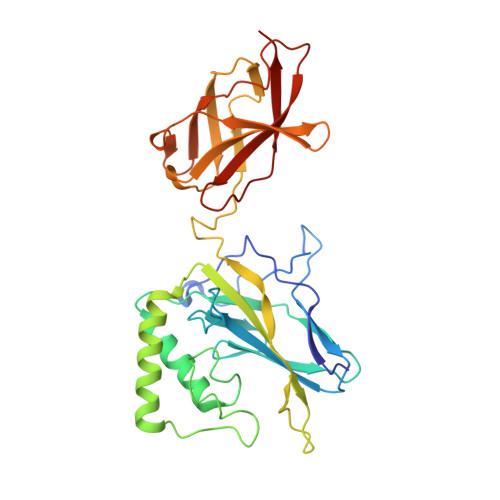
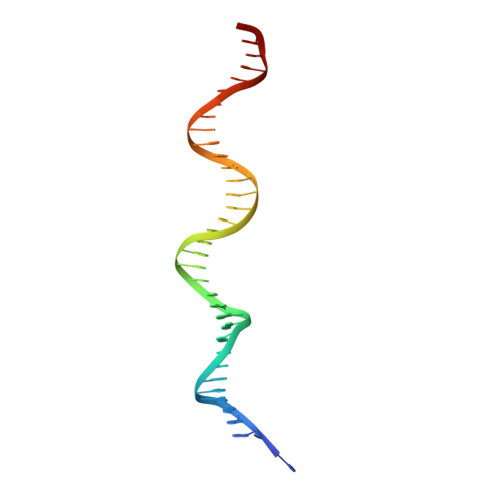
An Atomic Model of the Interferon-beta Enhanceosome.
Panne, D., Maniatis, T., Harrison, S.C.(2007) Cell 129: 1111-1123
- PubMed: 17574024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2O61, 2O6G - PubMed Abstract:
Transcriptional activation of the interferon-beta (IFN-beta) gene requires assembly of an enhanceosome containing ATF-2/c-Jun, IRF-3/IRF-7, and NFkappaB. These factors bind cooperatively to the IFN-beta enhancer and recruit coactivators and chromatin-remodeling proteins to the IFN-beta promoter. We describe here a crystal structure of the DNA-binding domains of IRF-3, IRF-7, and NFkappaB, bound to one half of the enhancer, and use a previously described structure of the remaining half to assemble a complete picture of enhanceosome architecture in the vicinity of the DNA. Association of eight proteins with the enhancer creates a continuous surface for recognizing a composite DNA-binding element. Paucity of local protein-protein contacts suggests that cooperative occupancy of the enhancer comes from both binding-induced changes in DNA conformation and interactions with additional components such as CBP. Contacts with virtually every nucleotide pair account for the evolutionary invariance of the enhancer sequence.
- The Jack and Eileen Connors Structural Biology Laboratory, Harvard Medical School, Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 250 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: