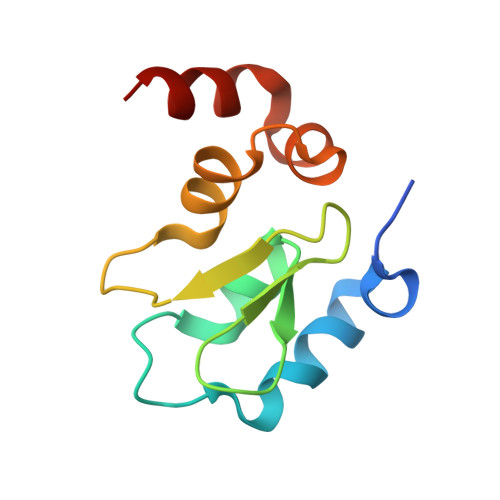
The structure of the BIR3 domain of cIAP1 in complex with the N-terminal peptides of SMAC and caspase-9.
Kulathila, R., Vash, B., Sage, D., Cornell-Kennon, S., Wright, K., Koehn, J., Stams, T., Clark, K., Price, A.(2009) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 65: 58-66
- PubMed: 19153467
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444908039243
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3D9T, 3D9U - PubMed Abstract:
The inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family of molecules inhibit apoptosis through the suppression of caspase activity. It is known that the XIAP protein regulates both caspase-3 and caspase-9 through direct protein-protein interactions. Specifically, the BIR3 domain of XIAP binds to caspase-9 via a ;hotspot' interaction in which the N-terminal residues of caspase-9 bind in a shallow groove on the surface of XIAP. This interaction is regulated via SMAC, the N-terminus of which binds in the same groove, thus displacing caspase-9. The mechanism of suppression of apoptosis by cIAP1 is less clear. The structure of the BIR3 domain of cIAP1 (cIAP1-BIR3) in complex with N-terminal peptides from both SMAC and caspase-9 has been determined. The binding constants of these peptides to cIAP1-BIR3 have also been determined using the surface plasmon resonance technique. The structures show that the peptides interact with cIAP1 in the same way that they interact with XIAP: both peptides bind in a similar shallow groove in the BIR3 surface, anchored at the N-terminus by a charge-stabilized hydrogen bond. The binding data show that the SMAC and caspase-9 peptides bind with comparable affinities (85 and 48 nM, respectively).
- Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research Inc., USA.
Organizational Affiliation: