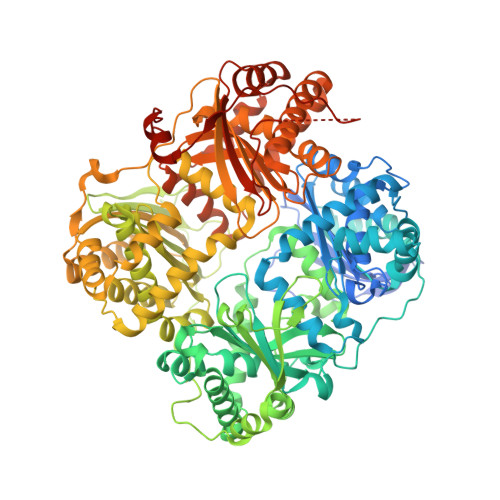
Designed inhibitors of insulin-degrading enzyme regulate the catabolism and activity of insulin.
Leissring, M.A., Malito, E., Hedouin, S., Reinstatler, L., Sahara, T., Abdul-Hay, S.O., Choudhry, S., Maharvi, G.M., Fauq, A.H., Huzarska, M., May, P.S., Choi, S., Logan, T.P., Turk, B.E., Cantley, L.C., Manolopoulou, M., Tang, W.J., Stein, R.L., Cuny, G.D., Selkoe, D.J.(2010) PLoS One 5: e10504-e10504
- PubMed: 20498699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010504
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3E4A - PubMed Abstract:
Insulin is a vital peptide hormone that is a central regulator of glucose homeostasis, and impairments in insulin signaling cause diabetes mellitus. In principle, it should be possible to enhance the activity of insulin by inhibiting its catabolism, which is mediated primarily by insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE), a structurally and evolutionarily distinctive zinc-metalloprotease. Despite interest in pharmacological inhibition of IDE as an attractive anti-diabetic approach dating to the 1950s, potent and selective inhibitors of IDE have not yet emerged. We used a rational design approach based on analysis of combinatorial peptide mixtures and focused compound libraries to develop novel peptide hydroxamic acid inhibitors of IDE. The resulting compounds are approximately 10(6) times more potent than existing inhibitors, non-toxic, and surprisingly selective for IDE vis-à-vis conventional zinc-metalloproteases. Crystallographic analysis of an IDE-inhibitor complex reveals a novel mode of inhibition based on stabilization of IDE's "closed," inactive conformation. We show further that pharmacological inhibition of IDE potentiates insulin signaling by a mechanism involving reduced catabolism of internalized insulin. The inhibitors we describe are the first to potently and selectively inhibit IDE or indeed any member of this atypical zinc-metalloprotease superfamily. The distinctive structure of IDE's active site, and the mode of action of our inhibitors, suggests that it may be possible to develop inhibitors that cross-react minimally with conventional zinc-metalloproteases. Significantly, our results reveal that insulin signaling is normally regulated by IDE activity not only extracellularly but also within cells, supporting the longstanding view that IDE inhibitors could hold therapeutic value for the treatment of diabetes.
- Department of Neuroscience, Mayo Clinic Florida, Jacksonville, Florida, United States of America. Leissring@mayo.edu
Organizational Affiliation: