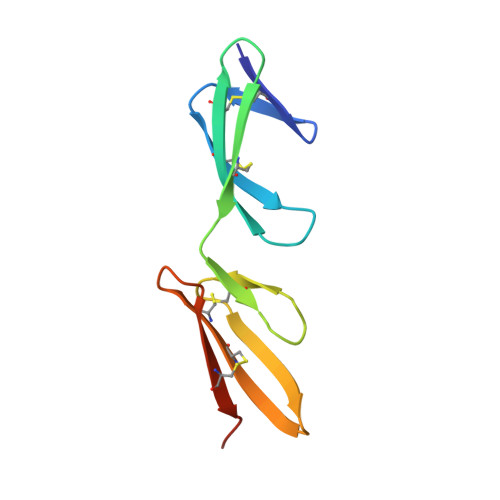
Structural analysis of collagen type I interactions with human fibronectin reveals a cooperative binding mode
Erat, M.C., Sladek, B., Campbell, I.D., Vakonakis, I.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 17441-17450
- PubMed: 23653354
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.469841
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GXE - PubMed Abstract:
Despite its biological importance, the interaction between fibronectin (FN) and collagen, two abundant and crucial tissue components, has not been well characterized on a structural level. Here, we analyzed the four interactions formed between epitopes of collagen type I and the collagen-binding fragment (gelatin-binding domain (GBD)) of human FN using solution NMR, fluorescence, and small angle x-ray scattering methods. Collagen association with FN modules (8-9)FnI occurs through a conserved structural mechanism but exhibits a 400-fold disparity in affinity between collagen sites. This disparity is reduced in the full-length GBD, as (6)FnI(1-2)FnII(7)FnI binds a specific collagen epitope next to the weakest (8-9)FnI-binding site. The cooperative engagement of all GBD modules with collagen results in four broadly equipotent FN-collagen interaction sites. Collagen association stabilizes a distinct monomeric GBD conformation in solution, giving further evidence to the view that FN fragments form well defined functional and structural units.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3QU, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: