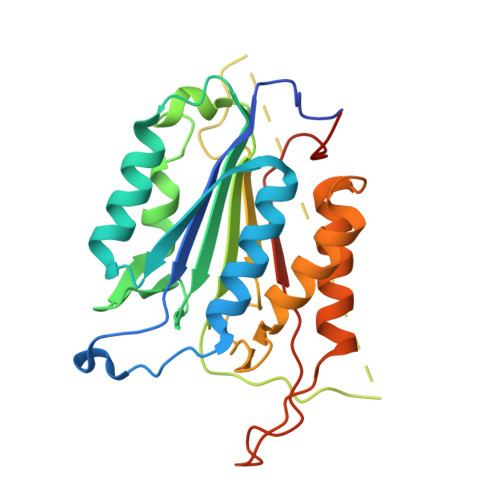
L2' loop is critical for caspase-7 active site formation.
Witkowski, W.A., Hardy, J.A.(2009) Protein Sci 18: 1459-1468
- PubMed: 19530232
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.151
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3H1P - PubMed Abstract:
The active sites of caspases are composed of four mobile loops. A loop (L2) from one half of the dimer interacts with a loop (L2') from the other half of the dimer to bind substrate. In an inactive form, the two L2' loops form a cross-dimer hydrogen-bond network over the dimer interface. Although the L2' loop has been implicated as playing a central role in the formation of the active-site loop bundle, its precise role in catalysis has not been shown. A detailed understanding of the active and inactive conformations is essential to control the caspase function. We have interrogated the contributions of the residues in the L2' loop to catalytic function and enzyme stability. In wild-type and all mutants, active-site binding results in substantial stabilization of the complex. One mutation, P214A, is significantly destabilized in the ligand-free conformation, but is as stable as wild type when bound to substrate, indicating that caspase-7 rests in different conformations in the absence and presence of substrate. Residues K212 and I213 in the L2' loop are shown to be essential for substrate-binding and thus proper catalytic function of the caspase. In the crystal structure of I213A, the void created by side-chain deletion is compensated for by rearrangement of tyrosine 211 to fill the void, suggesting that the requirements of substrate-binding are sufficiently strong to induce the active conformation. Thus, although the L2' loop makes no direct contacts with substrate, it is essential for buttressing the substrate-binding groove and is central to native catalytic efficiency.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, Massachusetts 01003, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: