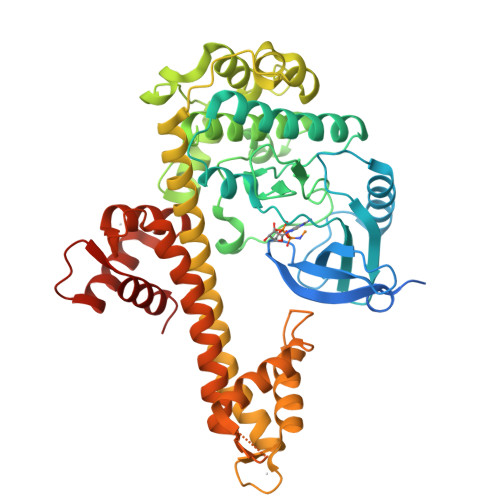
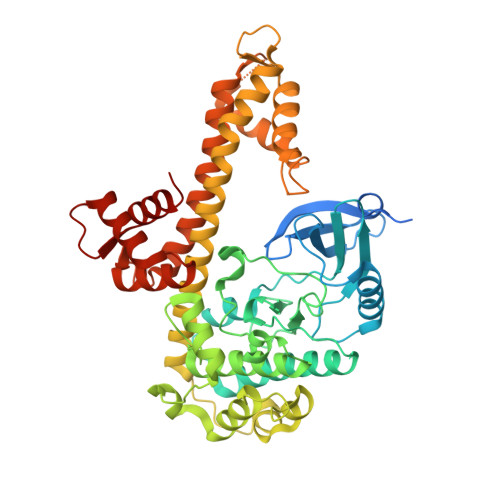
Structures of apicomplexan calcium-dependent protein kinases reveal mechanism of activation by calcium.
Wernimont, A.K., Artz, J.D., Finerty, P., Lin, Y.H., Amani, M., Allali-Hassani, A., Senisterra, G., Vedadi, M., Tempel, W., Mackenzie, F., Chau, I., Lourido, S., Sibley, L.D., Hui, R.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 596-601
- PubMed: 20436473
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1795
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HX4, 3HZT, 3IGO, 3KU2 - PubMed Abstract:
Calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs) have pivotal roles in the calcium-signaling pathway in plants, ciliates and apicomplexan parasites and comprise a calmodulin-dependent kinase (CaMK)-like kinase domain regulated by a calcium-binding domain in the C terminus. To understand this intramolecular mechanism of activation, we solved the structures of the autoinhibited (apo) and activated (calcium-bound) conformations of CDPKs from the apicomplexan parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium parvum. In the apo form, the C-terminal CDPK activation domain (CAD) resembles a calmodulin protein with an unexpected long helix in the N terminus that inhibits the kinase domain in the same manner as CaMKII. Calcium binding triggers the reorganization of the CAD into a highly intricate fold, leading to its relocation around the base of the kinase domain to a site remote from the substrate binding site. This large conformational change constitutes a distinct mechanism in calcium signal-transduction pathways.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.