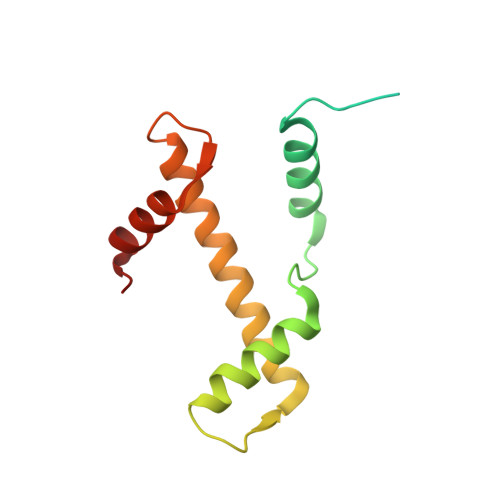
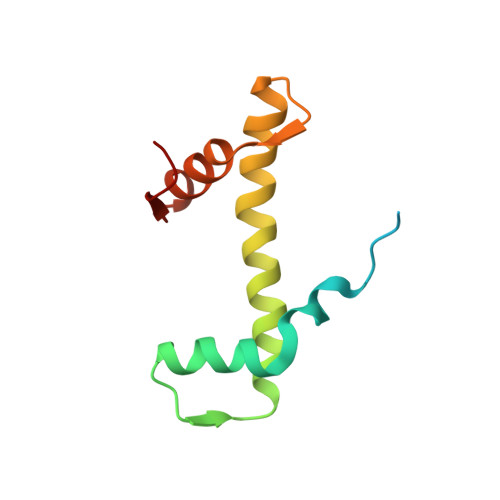
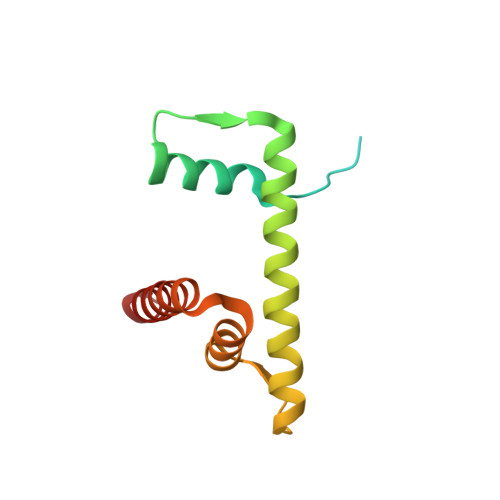
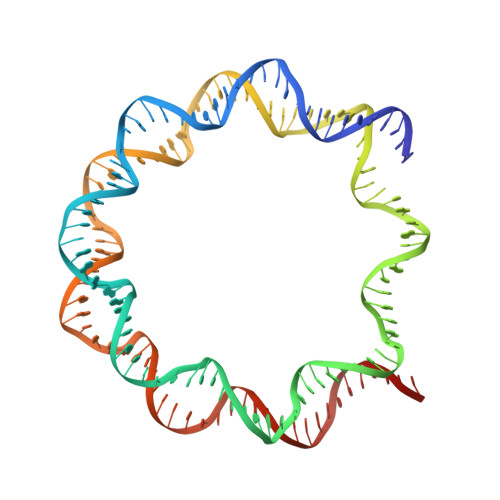
Crystal structures of nucleosome core particles containing the '601' strong positioning sequence
Vasudevan, D., Chua, E.Y., Davey, C.A.(2010) J Mol Biology 403: 1-10
- PubMed: 20800598
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.039
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LZ0, 3LZ1 - PubMed Abstract:
Nucleosome positioning plays a key role in genomic regulation by defining histone-DNA context and by modulating access to specific sites. Moreover, the histone-DNA register influences the double-helix structure, which in turn can affect the association of small molecules and protein factors. Analysis of genomic and synthetic DNA has revealed sequence motifs that direct nucleosome positioning in vitro; thus, establishing the basis for the DNA sequence dependence of positioning would shed light on the mechanics of the double helix and its contribution to chromatin structure in vivo. However, acquisition of well-diffracting nucleosome core particle (NCP) crystals is extremely dependent on the DNA fragment used for assembly, and all previous NCP crystal structures have been based on human α-satellite sequences. Here, we describe the crystal structures of Xenopus NCPs containing one of the strongest known histone octamer binding and positioning sequences, the so-called '601' DNA. Two distinct 145-bp 601 crystal forms display the same histone-DNA register, which coincides with the occurrence of DNA stretching-overtwisting in both halves of the particle around five double-helical turns from the nucleosome center, giving the DNA an 'effective length' of 147 bp. As we have found previously with stretching around two turns from the nucleosome center for a centromere-based sequence, the terminal stretching observed in the 601 constructs is associated with extreme kinking into the minor groove at purine-purine (pyrimidine-pyrimidine) dinucleotide steps. In other contexts, these step types display an overall nonflexible behavior, which raises the possibility that DNA stretching in the nucleosome or extreme distortions in general have unique sequence dependency characteristics. Our findings indicate that DNA stretching is an intrinsically predisposed site-specific property of the nucleosome and suggest how NCP crystal structures with diverse DNA sequences can be obtained.
- Division of Structural and Computational Biology, School of Biological Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, 60 Nanyang Drive, Singapore 637551, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: