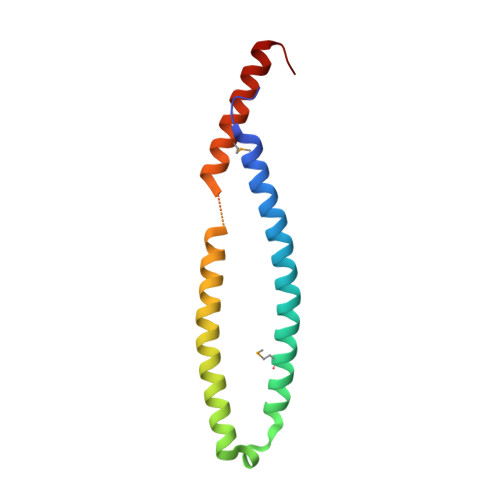
Coiled-Coil Domain-Dependent Homodimerization of Intracellular Barley Immune Receptors Defines a Minimal Functional Module for Triggering Cell Death
Maekawa, T., Cheng, W., Spiridon, L.N., Toller, A., Lukasik, E., Saijo, Y., Liu, P., Shen, Q.H., Micluta, M.A., Somssich, I.E., Takken, F.L., Petrescu, A.J., Chai, J., Schulze-Lefert, P.(2011) Cell Host Microbe 9: 187-199
- PubMed: 21402358
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2011.02.008
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QFL - PubMed Abstract:
Plants and animals have evolved structurally related innate immune sensors, designated NLRs, to detect intracellular nonself molecules. NLRs are modular, consisting of N-terminal coiled-coil (CC) or TOLL/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domains, a central nucleotide-binding (NB) domain, and C-terminal leucine-rich repeats (LRRs). The polymorphic barley mildew A (MLA) locus encodes CC-containing allelic immune receptors recognizing effectors of the pathogenic powdery mildew fungus. We report the crystal structure of an MLA receptor's invariant CC domain, which reveals a rod-shaped homodimer. MLA receptors also self-associate in vivo, but self-association appears to be independent of effector-triggered receptor activation. MLA CC mutants that fail to self-interact impair in planta cell death activity triggered by the CC domain alone and by an autoactive full-length MLA receptor that mimics its ATP-bound state. Thus, CC domain-dependent dimerization of the immune sensor defines a minimal functional unit and implies a role for the dimeric CC module in downstream immune signaling.
- Department of Plant-Microbe Interactions, Max-Planck Institut für Pflanzenzüchtungsforschung, Carl-von-Linne Weg 10, 50829 Cologne, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: