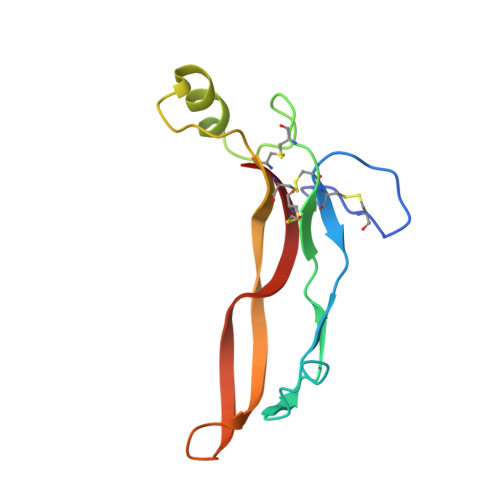
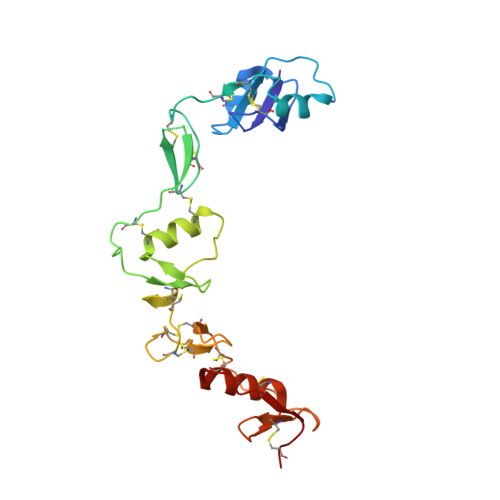
Structure of myostatinfollistatin-like 3: N-terminal domains of follistatin-type molecules exhibit alternate modes of binding.
Cash, J.N., Angerman, E.B., Kattamuri, C., Nolan, K., Zhao, H., Sidis, Y., Keutmann, H.T., Thompson, T.B.(2012) J Biological Chem 287: 1043-1053
- PubMed: 22052913
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.270801
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SEK - PubMed Abstract:
TGF-β family ligands are involved in a variety of critical physiological processes. For instance, the TGF-β ligand myostatin is a staunch negative regulator of muscle growth and a therapeutic target for muscle-wasting disorders. Therefore, it is important to understand the molecular mechanisms of TGF-β family regulation. One form of regulation is through inhibition by extracellular antagonists such as the follistatin (Fst)-type proteins. Myostatin is tightly controlled by Fst-like 3 (Fstl3), which is the only Fst-type molecule that has been identified in the serum bound to myostatin. Here, we present the crystal structure of myostatin in complex with Fstl3. The structure reveals that the N-terminal domain (ND) of Fstl3 interacts uniquely with myostatin as compared with activin A, because it utilizes different surfaces on the ligand. This results in conformational differences in the ND of Fstl3 that alter its position in the type I receptor-binding site of the ligand. We also show that single point mutations in the ND of Fstl3 are detrimental to ligand binding, whereas corresponding mutations in Fst have little effect. Overall, we have shown that the NDs of Fst-type molecules exhibit distinctive modes of ligand binding, which may affect overall affinity of ligand·Fst-type protein complexes.
- Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry, and Microbiology, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio 45267, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: