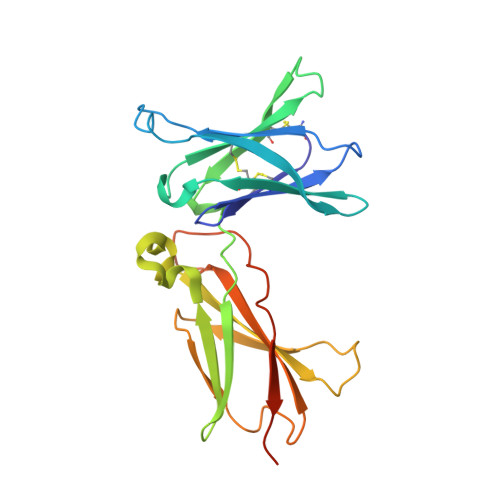
The crystal structure of the interleukin 21 receptor bound to interleukin 21 reveals that a sugar chain interacting with the WSXWS motif is an integral part of the interleukin 21 receptor.
Hamming, O.J., Kang, L., Svensson, A., Karlsen, J.L., Rahbek-Nielsen, H., Paludan, S.R., Hjorth, S.A., Bondensgaard, K., Hartmann, R.(2012) J Biological Chem
- PubMed: 22235133
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.311084
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TGX - PubMed Abstract:
IL-21 is a class I cytokine that exerts pleiotropic effects on both innate and adaptive immune responses. It signals through a heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of the IL-21 receptor (IL-21R) and the common γ-chain. A hallmark of the class I cytokine receptors is the class I cytokine receptor signature motif (WSXWS). The exact role of this motif has not been determined yet; however, it has been implicated in diverse functions, including ligand binding, receptor internalization, proper folding, and export, as well as signal transduction. Furthermore, the WXXW motif is known to be a consensus sequence for C-mannosylation. Here, we present the crystal structure of IL-21 bound to IL-21R and reveal that the WSXWS motif of IL-21R is C-mannosylated at the first tryptophan. We furthermore demonstrate that a sugar chain bridges the two fibronectin domains that constitute the extracellular domain of IL-21R and anchors at the WSXWS motif through an extensive hydrogen bonding network, including mannosylation. The glycan thus transforms the V-shaped receptor into an A-frame. This finding offers a novel structural explanation of the role of the class I cytokine signature motif.
- Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Aarhus University, Aarhus C, Denmark.
Organizational Affiliation: