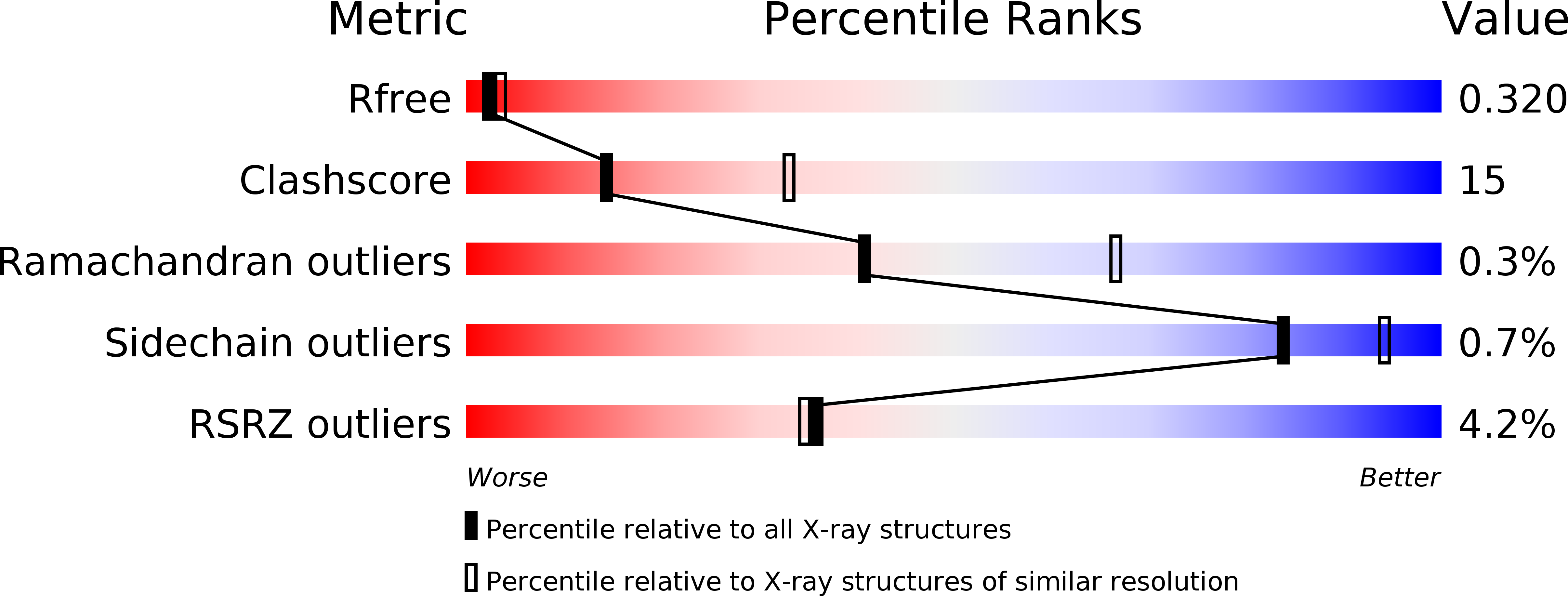
Identification and development of novel inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii enoyl reductase.
Tipparaju, S.K., Muench, S.P., Mui, E.J., Ruzheinikov, S.N., Lu, J.Z., Hutson, S.L., Kirisits, M.J., Prigge, S.T., Roberts, C.W., Henriquez, F.L., Kozikowski, A.P., Rice, D.W., McLeod, R.L.(2010) J Med Chem 53: 6287-6300
- PubMed: 20698542
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9017724
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NJ8 - PubMed Abstract:
Toxoplasmosis causes significant morbidity and mortality, and yet available medicines are limited by toxicities and hypersensitivity. Because improved medicines are needed urgently, rational approaches were used to identify novel lead compounds effective against Toxoplasma gondii enoyl reductase (TgENR), a type II fatty acid synthase enzyme essential in parasites but not present in animals. Fifty-three compounds, including three classes that inhibit ENRs, were tested. Six compounds have antiparasite MIC(90)s < or = 6 microM without toxicity to host cells, three compounds have IC(90)s < 45 nM against recombinant TgENR, and two protect mice. To further understand the mode of inhibition, the cocrystal structure of one of the most promising candidate compounds in complex with TgENR has been determined to 2.7 A. The crystal structure reveals that the aliphatic side chain of compound 19 occupies, as predicted, space made available by replacement of a bulky hydrophobic residue in homologous bacterial ENRs by Ala in TgENR. This provides a paradigm, conceptual foundation, reagents, and lead compounds for future rational development and discovery of improved inhibitors of T. gondii.
Organizational Affiliation:
Drug Discovery Program, Department of Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacognosy, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, USA.