Development of cyclic peptomer inhibitors targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1.
Murugan, R.N., Park, J.E., Lim, D., Ahn, M., Cheong, C., Kwon, T., Nam, K.Y., Choi, S.H., Kim, B.Y., Yoon, D.Y., Yaffe, M.B., Yu, D.Y., Lee, K.S., Bang, J.K.(2013) Bioorg Med Chem 21: 2623-2634
- PubMed: 23498919
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.02.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HAB, 4HY2 - PubMed Abstract:
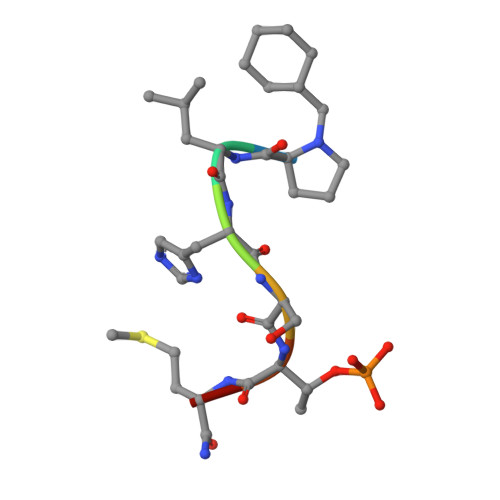
The polo-box domain (PBD) of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is essentially required for the function of Plk1 in cell proliferation. The availability of the phosphopeptide-binding pocket on PBD provides a unique opportunity to develop novel protein-protein interaction inhibitors. Recent identification of a minimal 5-residue-long phosphopeptide, PLHSpT, as a Plk1 PBD-specific ligand has led to the development of several peptide-based inhibitors, but none of them is cyclic peptide. Through the combination of single-peptoid mimics and thio-ether bridged cyclization, we successfully demonstrated for the first time two cyclic peptomers, PL-116 and PL-120, dramatically improved the binding affinity without losing mono-specificity against Plk1 PBD in comparison with the linear parental peptide, PLHSpT. These cyclic peptomers could serve as promising templates for future drug designs to inhibit Plk1 PBD.
- Division of Magnetic Resonance, Korea Basic Science Institute, Ochang, Chung-Buk 363-883, Cheongwon, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: