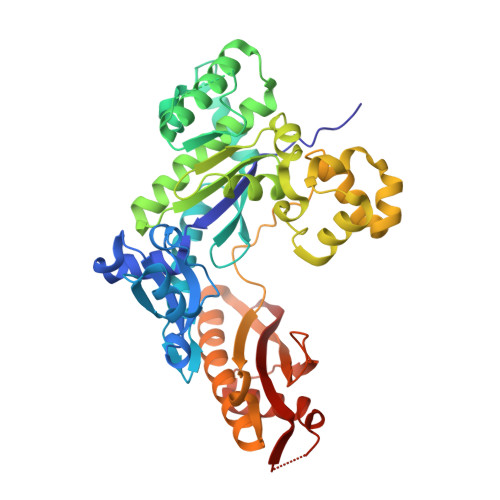
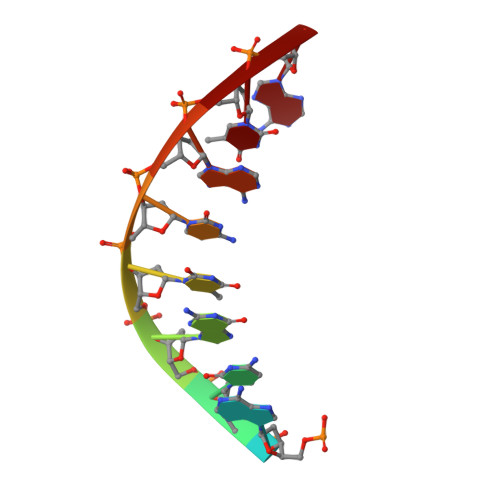
Mechanism of somatic hypermutation at the WA motif by human DNA polymerase eta.
Zhao, Y., Gregory, M.T., Biertumpfel, C., Hua, Y.J., Hanaoka, F., Yang, W.(2013) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 8146-8151
- PubMed: 23630267
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1303126110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4J9K, 4J9L, 4J9M, 4J9N, 4J9O, 4J9P, 4J9Q, 4J9R, 4J9S - PubMed Abstract:
Somatic hypermutation is programmed base substitutions in the variable regions of Ig genes for high-affinity antibody generation. Two motifs, RGYW and WA (R, purine; Y, pyrimidine; W, A or T), have been found to be somatic hypermutation hotspots. Overwhelming evidence suggests that DNA polymerase η (Pol η) is responsible for converting the WA motif to WG by misincorporating dGTP opposite the templating T. To elucidate the molecular mechanism, crystal structures and kinetics of human Pol η substituting dGTP for dATP in four sequence contexts, TA, AA, GA, and CA, have been determined and compared. The T:dGTP wobble base pair is stabilized by Gln-38 and Arg-61, two uniquely conserved residues among Pol η. Weak base paring of the W (T:A or A:T) at the primer end and their distinct interactions with Pol η lead to misincorporation of G in the WA motif. Between two WA motifs, our kinetic and structural data indicate that A-to-G mutation occurs more readily in the TA context than AA. Finally, Pol η can extend the T:G mispair efficiently to complete the mutagenesis.
- Institute of Nuclear-Agricultural Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310029, China.
Organizational Affiliation: