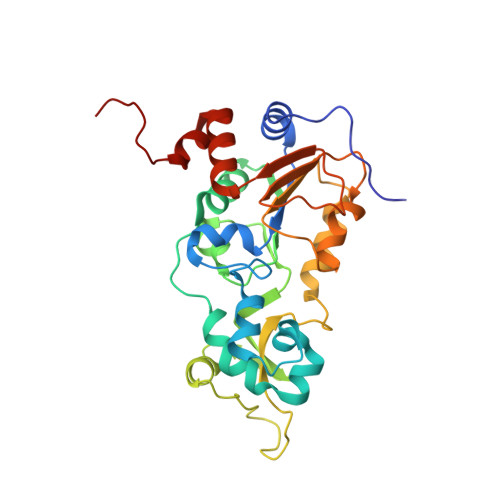
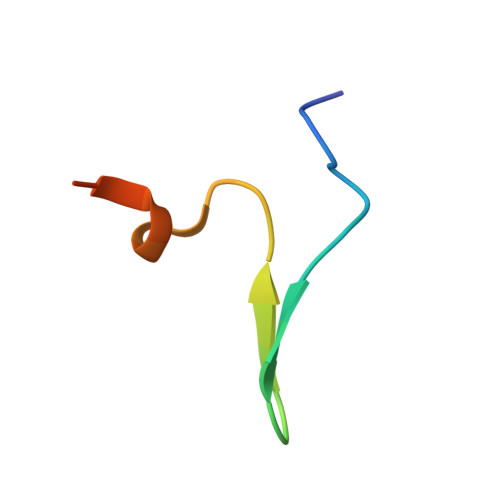
Structural and Functional Analysis of Human SIRT1.
Davenport, A.M., Huber, F.M., Hoelz, A.(2014) J Mol Biology 426: 526-541
- PubMed: 24120939
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2013.10.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4IG9, 4KXQ - PubMed Abstract:
SIRT1 is a NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase that plays important roles in many cellular processes. SIRT1 activity is uniquely controlled by a C-terminal regulatory segment (CTR). Here we present crystal structures of the catalytic domain of human SIRT1 in complex with the CTR in an open apo form and a closed conformation in complex with a cofactor and a pseudo-substrate peptide. The catalytic domain adopts the canonical sirtuin fold. The CTR forms a β hairpin structure that complements the β sheet of the NAD(+)-binding domain, covering an essentially invariant hydrophobic surface. The apo form adopts a distinct open conformation, in which the smaller subdomain of SIRT1 undergoes a rotation with respect to the larger NAD(+)-binding subdomain. A biochemical analysis identifies key residues in the active site, an inhibitory role for the CTR, and distinct structural features of the CTR that mediate binding and inhibition of the SIRT1 catalytic domain.
- Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: