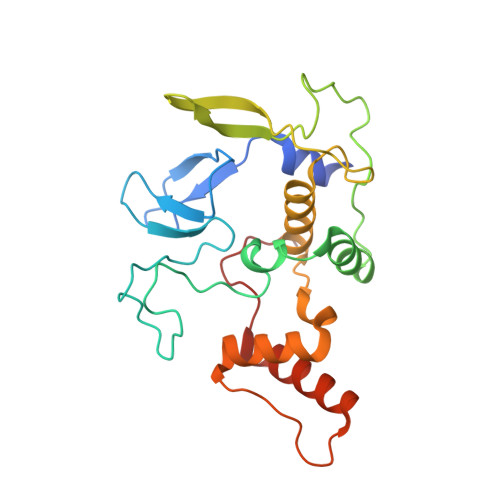
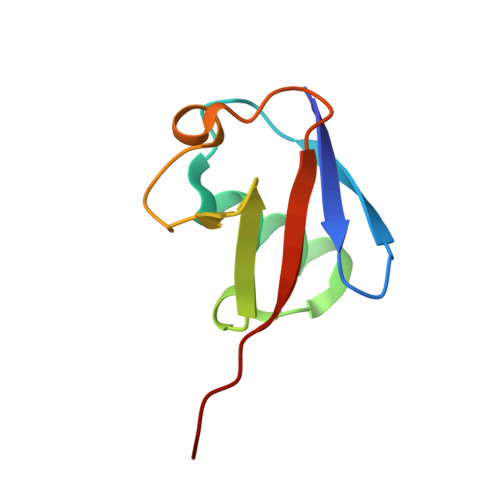
Structural basis for ligase-specific conjugation of linear ubiquitin chains by HOIP.
Stieglitz, B., Rana, R.R., Koliopoulos, M.G., Morris-Davies, A.C., Schaeffer, V., Christodoulou, E., Howell, S., Brown, N.R., Dikic, I., Rittinger, K.(2013) Nature 503: 422-426
- PubMed: 24141947
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12638
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LJO, 4LJP, 4LJQ - PubMed Abstract:
Linear ubiquitin chains are important regulators of cellular signalling pathways that control innate immunity and inflammation through nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation and protection against tumour necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis. They are synthesized by HOIP, which belongs to the RBR (RING-between-RING) family of E3 ligases and is the catalytic component of LUBAC (linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex), a multisubunit E3 ligase. RBR family members act as RING/HECT hybrids, employing RING1 to recognize ubiquitin-loaded E2 while a conserved cysteine in RING2 subsequently forms a thioester intermediate with the transferred or 'donor' ubiquitin. Here we report the crystal structure of the catalytic core of HOIP in its apo form and in complex with ubiquitin. The carboxy-terminal portion of HOIP adopts a novel fold that, together with a zinc-finger, forms a ubiquitin-binding platform that orients the acceptor ubiquitin and positions its α-amino group for nucleophilic attack on the E3∼ubiquitin thioester. The C-terminal tail of a second ubiquitin molecule is located in close proximity to the catalytic cysteine, providing a unique snapshot of the ubiquitin transfer complex containing both donor and acceptor ubiquitin. These interactions are required for activation of the NF-κB pathway in vivo, and they explain the determinants of linear ubiquitin chain specificity by LUBAC.
- Division of Molecular Structure, MRC-National Institute for Medical Research, The Ridgeway, London NW7 1AA, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: