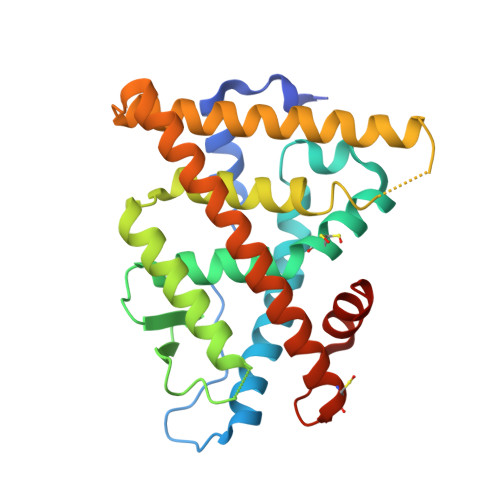
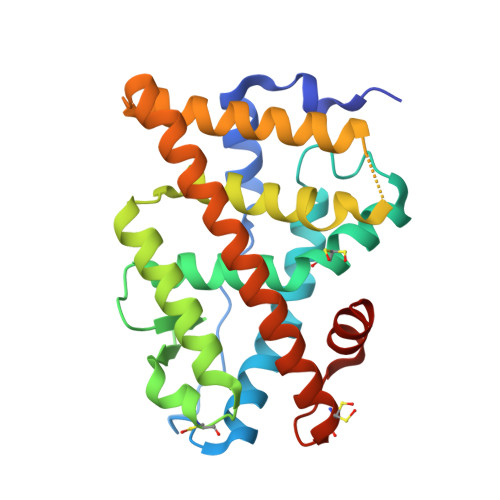
Structural and functional profiling of environmental ligands for estrogen receptors.
Delfosse, V., Grimaldi, M., Cavailles, V., Balaguer, P., Bourguet, W.(2014) Environ Health Perspect 122: 1306-1313
- PubMed: 25260197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408453
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4MG5, 4MG6, 4MG7, 4MG8, 4MG9, 4MGA, 4MGB, 4MGC, 4MGD - PubMed Abstract:
Individuals are exposed daily to environmental pollutants that may act as endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), causing a range of developmental, reproductive, metabolic, or neoplastic diseases. With their mostly hydrophobic pocket that serves as a docking site for endogenous and exogenous ligands, nuclear receptors (NRs) can be primary targets of small molecule environmental contaminants. However, most of these compounds are chemically unrelated to natural hormones, so their binding modes and associated hormonal activities are hardly predictable. We conducted a correlative analysis of structural and functional data to gain insight into the mechanisms by which 12 members of representative families of pollutants bind to and activate the estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ. We used a battery of biochemical, structural, biophysical, and cell-based approaches to characterize the interaction between ERs and their environmental ligands. Our study revealed that the chemically diverse compounds bound to ERs via varied sets of protein-ligand interactions, reflecting their differential activities, binding affinities, and specificities. We observed xenoestrogens binding to both ERs-with affinities ranging from subnanomolar to micromolar values-and acting in a subtype-dependent fashion as full agonists or partial agonists/antagonists by using different combinations of the activation functions 1 and 2 of ERα and ERβ. The precise characterization of the interactions between major environmental pollutants and two of their primary biological targets provides rational guidelines for the design of safer chemicals, and will increase the accuracy and usefulness of structure-based computational methods, allowing for activity prediction of chemicals in risk assessment.
- Inserm (Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale) U1054, Montpellier, France.
Organizational Affiliation: