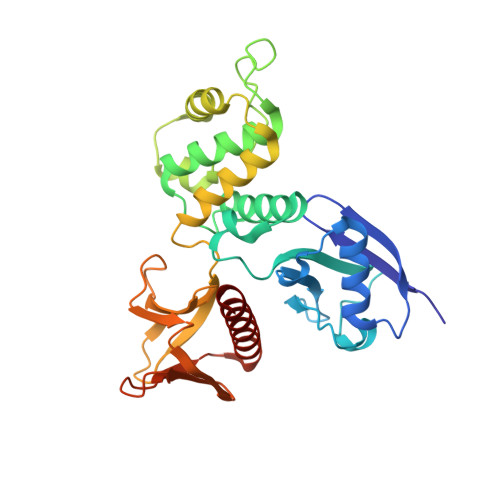
Structural characterization suggests models for monomeric and dimeric forms of full-length ezrin.
Phang, J.M., Harrop, S.J., Duff, A.P., Sokolova, A.V., Crossett, B., Walsh, J.C., Beckham, S.A., Nguyen, C.D., Davies, R.B., Glockner, C., Bromley, E.H., Wilk, K.E., Curmi, P.M.(2016) Biochem J 473: 2763-2782
- PubMed: 27364155
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160541
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4RM8, 4RM9, 4RMA - PubMed Abstract:
Ezrin is a member of the ERM (ezrin-radixin-moesin) family of proteins that have been conserved through metazoan evolution. These proteins have dormant and active forms, where the latter links the actin cytoskeleton to membranes. ERM proteins have three domains: an N-terminal FERM [band Four-point-one (4.1) ERM] domain comprising three subdomains (F1, F2, and F3); a helical domain; and a C-terminal actin-binding domain. In the dormant form, FERM and C-terminal domains form a stable complex. We have determined crystal structures of the active FERM domain and the dormant FERM:C-terminal domain complex of human ezrin. We observe a bistable array of phenylalanine residues in the core of subdomain F3 that is mobile in the active form and locked in the dormant form. As subdomain F3 is pivotal in binding membrane proteins and phospholipids, these transitions may facilitate activation and signaling. Full-length ezrin forms stable monomers and dimers. We used small-angle X-ray scattering to determine the solution structures of these species. As expected, the monomer shows a globular domain with a protruding helical coiled coil. The dimer shows an elongated dumbbell structure that is twice as long as the monomer. By aligning ERM sequences spanning metazoan evolution, we show that the central helical region is conserved, preserving the heptad repeat. Using this, we have built a dimer model where each monomer forms half of an elongated antiparallel coiled coil with domain-swapped FERM:C-terminal domain complexes at each end. The model suggests that ERM dimers may bind to actin in a parallel fashion.
- School of Physics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: