The crystal structure of alpha-thrombin-hirunorm IV complex reveals a novel specificity site recognition mode.
Lombardi, A., De Simone, G., Nastri, F., Galdiero, S., Della Morte, R., Staiano, N., Pedone, C., Bolognesi, M., Pavone, V.(1999) Protein Sci 8: 91-95
- PubMed: 10210187
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.8.1.91
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4THN - PubMed Abstract:
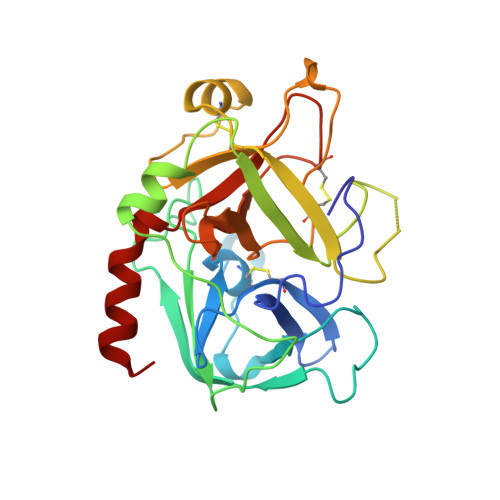
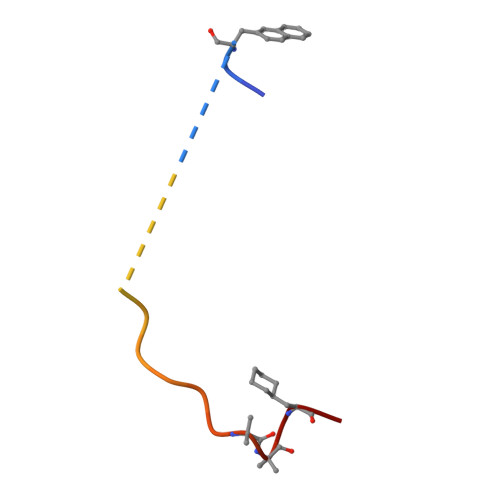
The X-ray crystal structure of the human alpha-thrombin-hirunorm IV complex has been determined at 2.5 A resolution, and refined to an R-factor of 0.173. The structure reveals an inhibitor binding mode distinctive of a true hirudin mimetic, which justifies the high inhibitory potency and the selectivity of hirunorm IV. This novel inhibitor, composed of 26 amino acids, interacts through the N-terminal end with the alpha-thrombin active site in a nonsubstrate mode, and binds specifically to the fibrinogen recognition exosite through the C-terminal end. The backbone of the N-terminal tripeptide Chg1"-Arg2"-2Na13" (Chg, cyclohexyl-glycine; 2Na1, beta-(2-naphthyl)-alanine) forms a parallel beta-strand to the thrombin main-chain segment Ser214-Gly216. The Chg1" side chain occupies the S2 site, Arg2" penetrates into the S1 specificity site, while the 2Na13" side chain occupies the aryl binding site. The Arg2" side chain enters the S1 specificity pocket from a position quite apart from the canonical P1 site. This notwithstanding, the Arg2" side chain establishes the typical ion pair with the carboxylate group of Asp189.
- Centro Interuniversitario di Ricerca su Peptidi Bioattivi & Centro di Studio di Biocristallografia-CNR, University of Napoli Federico II, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: