A selective chemical probe for exploring the role of CDK8 and CDK19 in human disease.
Dale, T., Clarke, P.A., Esdar, C., Waalboer, D., Adeniji-Popoola, O., Ortiz-Ruiz, M.J., Mallinger, A., Samant, R.S., Czodrowski, P., Musil, D., Schwarz, D., Schneider, K., Stubbs, M., Ewan, K., Fraser, E., TePoele, R., Court, W., Box, G., Valenti, M., de Haven Brandon, A., Gowan, S., Rohdich, F., Raynaud, F., Schneider, R., Poeschke, O., Blaukat, A., Workman, P., Schiemann, K., Eccles, S.A., Wienke, D., Blagg, J.(2015) Nat Chem Biol 11: 973-980
- PubMed: 26502155
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1952
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5BNJ - PubMed Abstract:
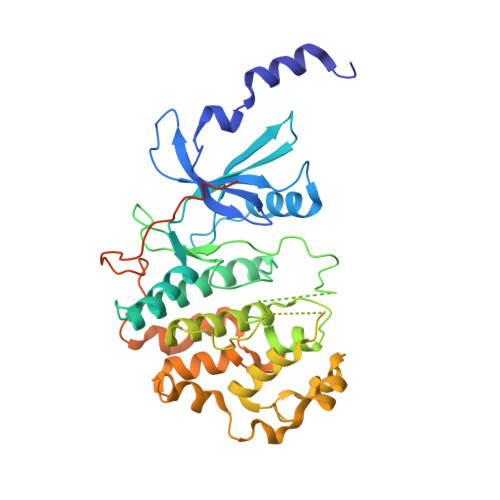
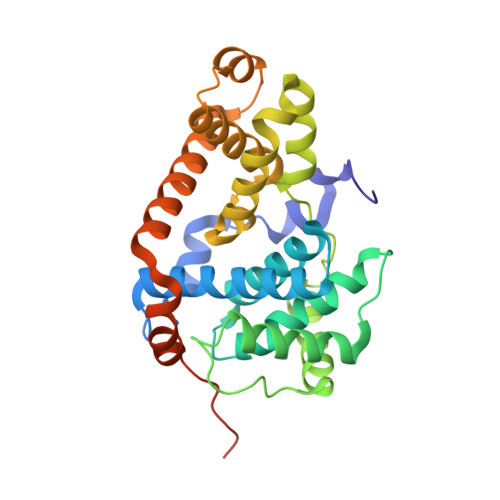
There is unmet need for chemical tools to explore the role of the Mediator complex in human pathologies ranging from cancer to cardiovascular disease. Here we determine that CCT251545, a small-molecule inhibitor of the WNT pathway discovered through cell-based screening, is a potent and selective chemical probe for the human Mediator complex-associated protein kinases CDK8 and CDK19 with >100-fold selectivity over 291 other kinases. X-ray crystallography demonstrates a type 1 binding mode involving insertion of the CDK8 C terminus into the ligand binding site. In contrast to type II inhibitors of CDK8 and CDK19, CCT251545 displays potent cell-based activity. We show that CCT251545 and close analogs alter WNT pathway-regulated gene expression and other on-target effects of modulating CDK8 and CDK19, including expression of genes regulated by STAT1. Consistent with this, we find that phosphorylation of STAT1(SER727) is a biomarker of CDK8 kinase activity in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we demonstrate in vivo activity of CCT251545 in WNT-dependent tumors.
- School of Bioscience, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: