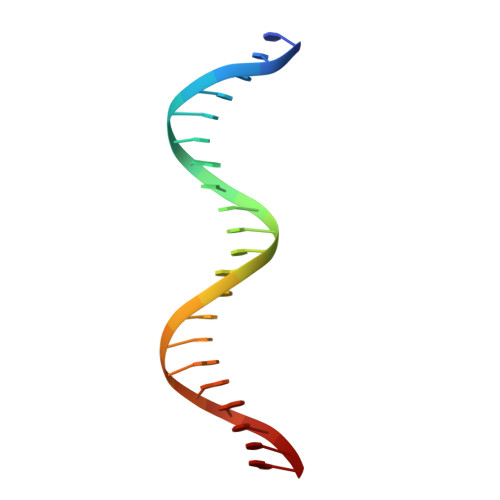
Crystal structures reveal a new and novel FoxO1 binding site within the human glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1 gene promoter.
Singh, P., Han, E.H., Endrizzi, J.A., O'Brien, R.M., Chi, Y.I.(2017) J Struct Biol 198: 54-64
- PubMed: 28223045
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2017.02.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5DUI - PubMed Abstract:
Human glucose-6-phosphatase plays a vital role in blood glucose homeostasis and holds promise as a therapeutic target for diabetes. Expression of its catalytic subunit gene 1 (G6PC1) is tightly regulated by metabolic-response transcription factors such as FoxO1 and CREB. Although at least three potential FoxO1 binding sites (insulin response elements, IREs) and one CREB binding site (cAMP response element, CRE) within the proximal region of the G6PC1 promoter have been identified, the interplay between FoxO1 and CREB and between FoxO1 bound at multiple IREs has not been well characterized. Here we present the crystal structures of the FoxO1 DNA binding domain in complex with the G6PC1 promoter. These complexes reveal the presence of a new non-consensus FoxO1 binding site that overlaps the CRE, suggesting a mutual exclusion mechanism for FoxO1 and CREB binding at the G6PC1 promoter. Additional findings include (i) non-canonical FoxO1 recognition sites, (ii) incomplete FoxO1 occupancies at the available IRE sites, and (iii) FoxO1 dimeric interactions that may play a role in stabilizing DNA looping. These findings provide insight into the regulation of G6PC1 gene transcription by FoxO1, and demonstrate a high versatility of target gene recognition by FoxO1 that correlates with its diverse roles in biology.
- Section of Structural Biology, Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, MN 55912, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: