Structural Basis of Inhibition of ER alpha-Coactivator Interaction by High-Affinity N-Terminus Isoaspartic Acid Tethered Helical Peptides
Xie, M., Zhao, H., Liu, Q., Zhu, Y., Yin, F., Liang, Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, D., Hu, K., Qin, X., Wang, Z., Wu, Y., Xu, N., Ye, X., Wang, T., Li, Z.(2017) J Med Chem 60: 8731-8740
- PubMed: 29045135
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00732
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GS4, 5GTR - PubMed Abstract:
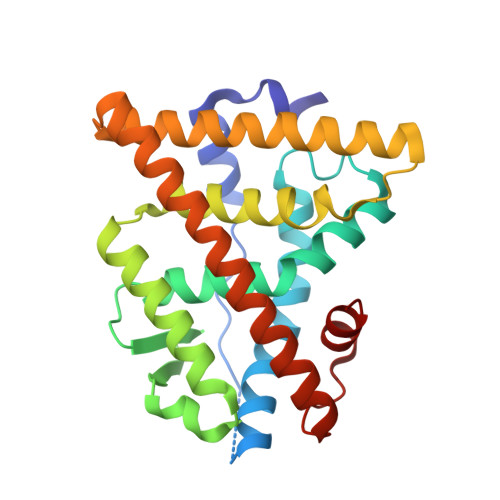
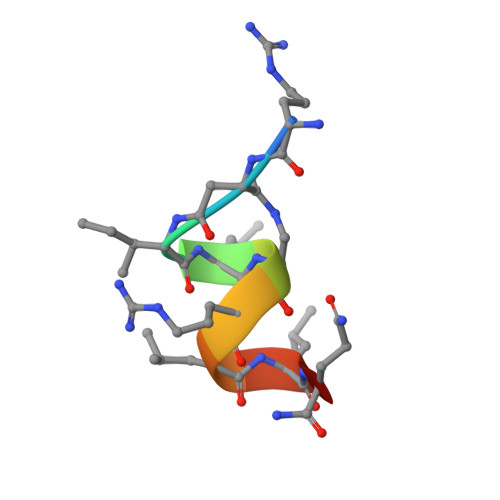
Direct inhibition of the protein-protein interaction of ERα and its endogenous coactivators with a cell permeable stabilized peptide may offer a novel, promising strategy for combating ERα positive breast cancers. Here, we report the co-crystal structure of a helical peptide stabilized by a N-terminal unnatural cross-linked aspartic acid (TD) in complex with the ERα ligand binding domain (LBD). We designed a series of peptides and peptide 6 that showed direct and high-affinity binding to ERα with selective antiproliferative activity in ERα positive breast cancer cells. The co-crystal structure of the TD-stabilized peptide 6 in complex with ERα LBD further demonstrates that it forms an α helical conformation and directly binds at the coactivator binding site of ERα. Further studies showed that peptide 6 W could potently inhibit cellular ERα's transcriptional activity. This approach demonstrates the potential of TD stabilized peptides to modulate various intracellular protein-protein interactions involved in a range of disorders.
- School of Chemical Biology and Biotechnology, Shenzhen Graduate School of Peking University , Shenzhen 518055, China.
Organizational Affiliation: