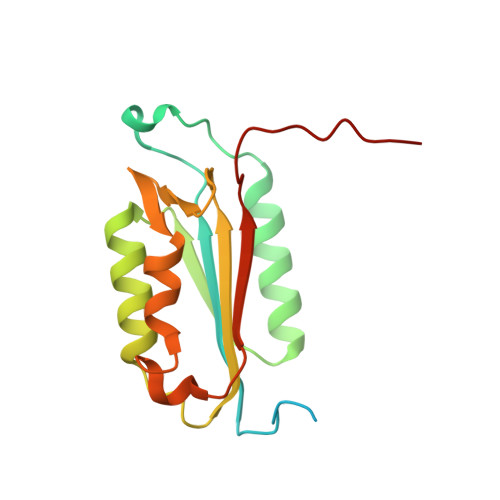
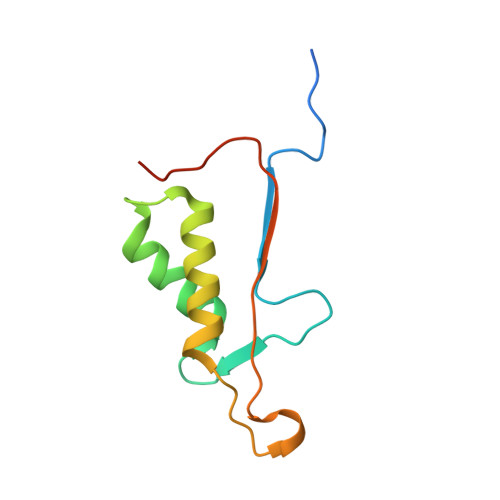
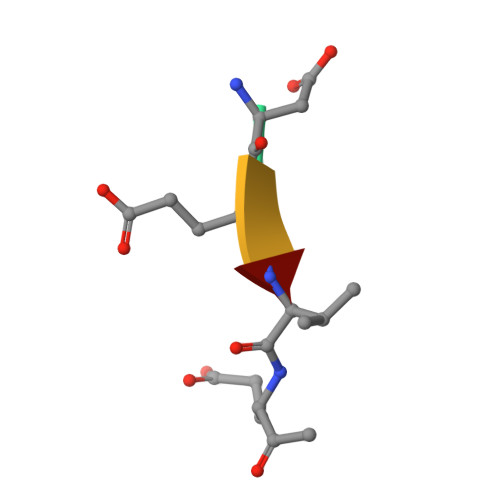
Cacidases: caspases can cleave after aspartate, glutamate and phosphoserine residues.
Seaman, J.E., Julien, O., Lee, P.S., Rettenmaier, T.J., Thomsen, N.D., Wells, J.A.(2016) Cell Death Differ 23: 1717-1726
- PubMed: 27367566
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.62
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5IC4, 5IC6 - PubMed Abstract:
Caspases are a family of proteases found in all metazoans, including a dozen in humans, that drive the terminal stages of apoptosis as well as other cellular remodeling and inflammatory events. Caspases are named because they are cysteine class enzymes shown to cleave after aspartate residues. In the past decade, we and others have developed unbiased proteomic methods that collectively identified ~2000 native proteins cleaved during apoptosis after the signature aspartate residues. Here, we explore non-aspartate cleavage events and identify 100s of substrates cleaved after glutamate in both human and murine apoptotic samples. The extended consensus sequence patterns are virtually identical for the aspartate and glutamate cleavage sites suggesting they are cleaved by the same caspases. Detailed kinetic analyses of the dominant apoptotic executioner caspases-3 and -7 show that synthetic substrates containing DEVD↓ are cleaved only twofold faster than DEVE↓, which is well within the 500-fold range of rates that natural proteins are cut. X-ray crystallography studies confirm that the two acidic substrates bind in virtually the same way to either caspases-3 or -7 with minimal adjustments to accommodate the larger glutamate. Lastly, during apoptosis we found 121 proteins cleaved after serine residues that have been previously annotated to be phosphorylation sites. We found that caspase-3, but not caspase-7, can cleave peptides containing DEVpS↓ at only threefold slower rate than DEVD↓, but does not cleave the unphosphorylated serine peptide. There are only a handful of previously reported examples of proteins cleaved after glutamate and none after phosphorserine. Our studies reveal a much greater promiscuity for cleaving after acidic residues and the name 'cacidase' could aptly reflect this broader specificity.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: