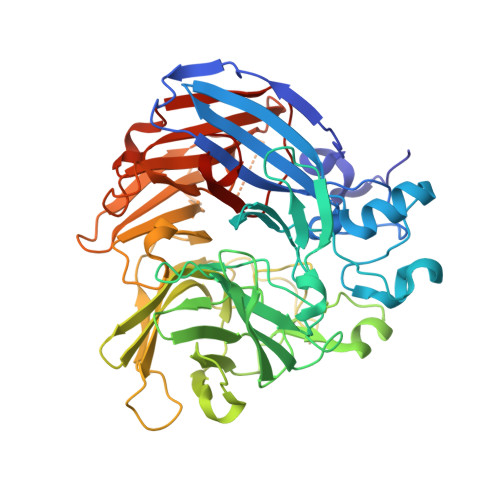
Structure and mechanism of NOV1, a resveratrol-cleaving dioxygenase.
McAndrew, R.P., Sathitsuksanoh, N., Mbughuni, M.M., Heins, R.A., Pereira, J.H., George, A., Sale, K.L., Fox, B.G., Simmons, B.A., Adams, P.D.(2016) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113: 14324-14329
- PubMed: 27911781
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1608917113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5J53, 5J54, 5J55 - PubMed Abstract:
Stilbenes are diphenyl ethene compounds produced naturally in a wide variety of plant species and some bacteria. Stilbenes are also derived from lignin during kraft pulping. Stilbene cleavage oxygenases (SCOs) cleave the central double bond of stilbenes, forming two phenolic aldehydes. Here, we report the structure of an SCO. The X-ray structure of NOV1 from Novosphingobium aromaticivorans was determined in complex with its substrate resveratrol (1.89 Å), its product vanillin (1.75 Å), and without any bound ligand (1.61 Å). The enzyme is a seven-bladed β-propeller with an iron cofactor coordinated by four histidines. In all three structures, dioxygen is observed bound to the iron in a side-on fashion. These structures, along with EPR analysis, allow us to propose a mechanism in which a ferric-superoxide reacts with substrate activated by deprotonation of a phenol group at position 4 of the substrate, which allows movement of electron density toward the central double bond and thus facilitates reaction with the ferric superoxide electrophile. Correspondingly, NOV1 cleaves a wide range of other stilbene-like compounds with a 4'-OH group, offering potential in processing some solubilized fragments of lignin into monomer aromatic compounds.
- Joint BioEnergy Institute, Emeryville, CA 94608; rpmcandrew@lbl.gov PDAdams@lbl.gov.
Organizational Affiliation: