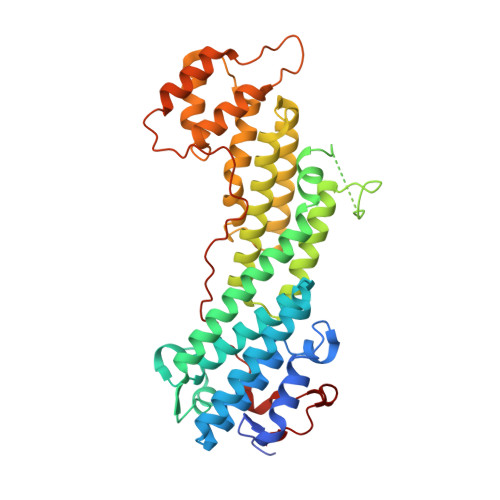
Coordinated recruitment of Spir actin nucleators and myosin V motors to Rab11 vesicle membranes.
Pylypenko, O., Welz, T., Tittel, J., Kollmar, M., Chardon, F., Malherbe, G., Weiss, S., Michel, C.I., Samol-Wolf, A., Grasskamp, A.T., Hume, A., Goud, B., Baron, B., England, P., Titus, M.A., Schwille, P., Weidemann, T., Houdusse, A., Kerkhoff, E.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 27623148
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.17523
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JCY, 5JCZ - PubMed Abstract:
There is growing evidence for a coupling of actin assembly and myosin motor activity in cells. However, mechanisms for recruitment of actin nucleators and motors on specific membrane compartments remain unclear. Here we report how Spir actin nucleators and myosin V motors coordinate their specific membrane recruitment. The myosin V globular tail domain (MyoV-GTD) interacts directly with an evolutionarily conserved Spir sequence motif. We determined crystal structures of MyoVa-GTD bound either to the Spir-2 motif or to Rab11 and show that a Spir-2:MyoVa:Rab11 complex can form. The ternary complex architecture explains how Rab11 vesicles support coordinated F-actin nucleation and myosin force generation for vesicle transport and tethering. New insights are also provided into how myosin activation can be coupled with the generation of actin tracks. Since MyoV binds several Rab GTPases, synchronized nucleator and motor targeting could provide a common mechanism to control force generation and motility in different cellular processes.
- Institut Curie, PSL Research University, CNRS, UMR 144, F-75005, Paris, France.
Organizational Affiliation: