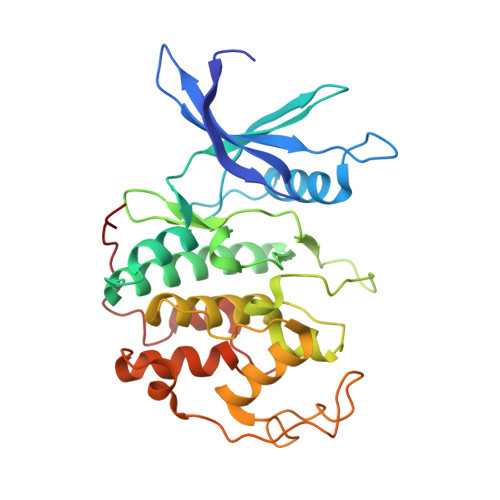
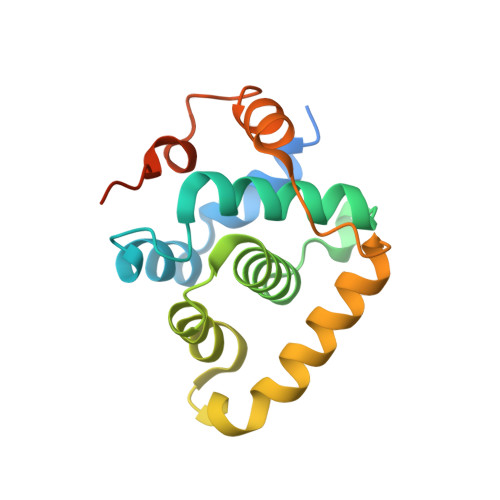
Structural basis of divergent cyclin-dependent kinase activation by Spy1/RINGO proteins.
McGrath, D.A., Fifield, B.A., Marceau, A.H., Tripathi, S., Porter, L.A., Rubin, S.M.(2017) EMBO J 36: 2251-2262
- PubMed: 28666995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201796905
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UQ1, 5UQ2, 5UQ3 - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) are principal drivers of cell division and are an important therapeutic target to inhibit aberrant proliferation. Cdk enzymatic activity is tightly controlled through cyclin interactions, posttranslational modifications, and binding of inhibitors such as the p27 tumor suppressor protein. Spy1/RINGO (Spy1) proteins bind and activate Cdk but are resistant to canonical regulatory mechanisms that establish cell-cycle checkpoints. Cancer cells exploit Spy1 to stimulate proliferation through inappropriate activation of Cdks, yet the mechanism is unknown. We have determined crystal structures of the Cdk2-Spy1 and p27-Cdk2-Spy1 complexes that reveal how Spy1 activates Cdk. We find that Spy1 confers structural changes to Cdk2 that obviate the requirement of Cdk activation loop phosphorylation. Spy1 lacks the cyclin-binding site that mediates p27 and substrate affinity, explaining why Cdk-Spy1 is poorly inhibited by p27 and lacks specificity for substrates with cyclin-docking sites. We identify mutations in Spy1 that ablate its ability to activate Cdk2 and to proliferate cells. Our structural description of Spy1 provides important mechanistic insights that may be utilized for targeting upregulated Spy1 in cancer.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: