Potent and selective antitumor activity of a T cell-engaging bispecific antibody targeting a membrane-proximal epitope of ROR1.
Qi, J., Li, X., Peng, H., Cook, E.M., Dadashian, E.L., Wiestner, A., Park, H., Rader, C.(2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115: E5467-E5476
- PubMed: 29844189
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719905115
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BA5, 6BAN - PubMed Abstract:
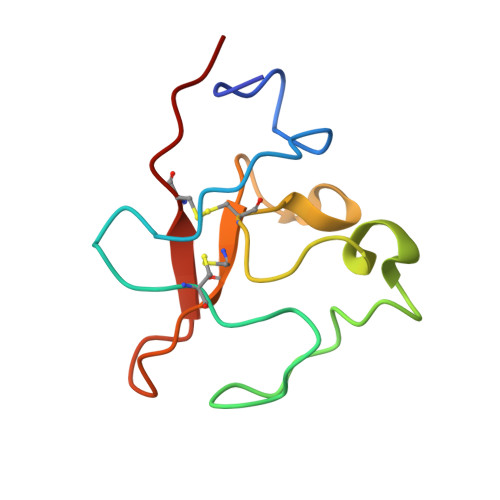
T cell-engaging bispecific antibodies (biAbs) present a promising strategy for cancer immunotherapy, and numerous bispecific formats have been developed for retargeting cytolytic T cells toward tumor cells. To explore the therapeutic utility of T cell-engaging biAbs targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1, which is expressed by tumor cells of various hematologic and solid malignancies, we used a bispecific ROR1 × CD3 scFv-Fc format based on a heterodimeric and aglycosylated Fc domain designed for extended circulatory t 1/2 and diminished systemic T cell activation. A diverse panel of ROR1-targeting scFv derived from immune and naïve rabbit antibody repertoires was compared in this bispecific format for target-dependent T cell recruitment and activation. An ROR1-targeting scFv with a membrane-proximal epitope, R11, revealed potent and selective antitumor activity in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo and emerged as a prime candidate for further preclinical and clinical studies. To elucidate the precise location and engagement of this membrane-proximal epitope, which is conserved between human and mouse ROR1, the 3D structure of scFv R11 in complex with the kringle domain of ROR1 was determined by X-ray crystallography at 1.6-Å resolution.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Immunology and Microbiology, The Scripps Research Institute, Jupiter, FL 33458.