Structural basis of malodour precursor transport in the human axilla.
Minhas, G.S., Bawdon, D., Herman, R., Rudden, M., Stone, A.P., James, A.G., Thomas, G.H., Newstead, S.(2018) Elife 7
- PubMed: 29966586
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34995
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
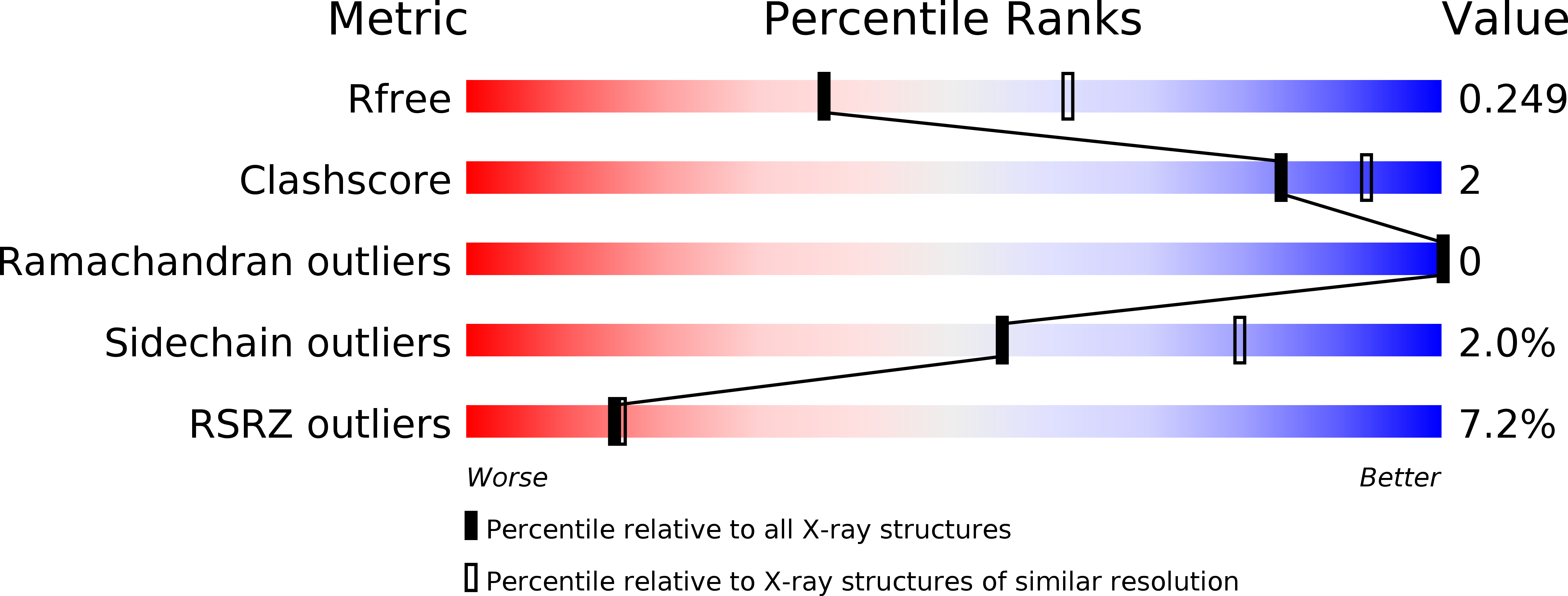
6EXS - PubMed Abstract:
Mammals produce volatile odours that convey different types of societal information. In Homo sapiens , this is now recognised as body odour, a key chemical component of which is the sulphurous thioalcohol, 3-methyl-3-sulfanylhexan-1-ol (3M3SH). Volatile 3M3SH is produced in the underarm as a result of specific microbial activity, which act on the odourless dipeptide-containing malodour precursor molecule, S-Cys-Gly-3M3SH, secreted in the axilla (underarm) during colonisation. The mechanism by which these bacteria recognise S-Cys-Gly-3M3SH and produce body odour is still poorly understood. Here we report the structural and biochemical basis of bacterial transport of S-Cys-Gly-3M3SH by Staphylococcus hominis , which is converted to the sulphurous thioalcohol component 3M3SH in the bacterial cytoplasm, before being released into the environment. Knowledge of the molecular basis of precursor transport, essential for body odour formation, provides a novel opportunity to design specific inhibitors of malodour production in humans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom.