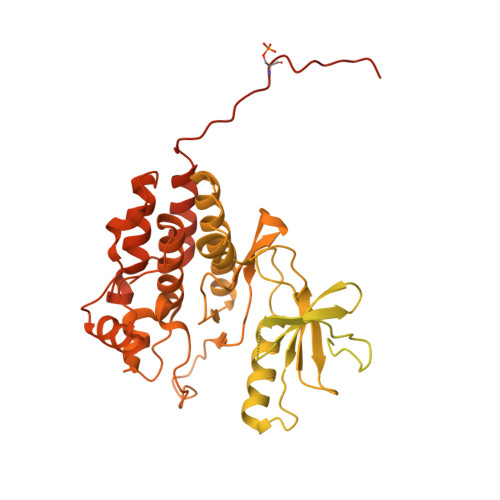
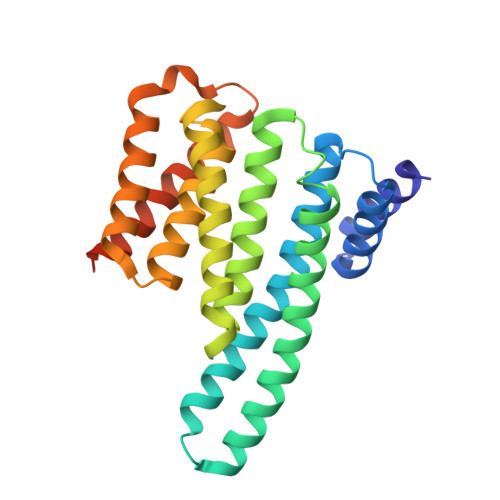
Architecture of autoinhibited and active BRAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes.
Park, E., Rawson, S., Li, K., Kim, B.W., Ficarro, S.B., Pino, G.G., Sharif, H., Marto, J.A., Jeon, H., Eck, M.J.(2019) Nature 575: 545-550
- PubMed: 31581174
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1660-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NYB, 6PP9, 6Q0J, 6Q0K, 6Q0T - PubMed Abstract:
RAF family kinases are RAS-activated switches that initiate signalling through the MAP kinase cascade to control cellular proliferation, differentiation and survival 1-3 . RAF activity is tightly regulated and inappropriate activation is a frequent cause of cancer 4-6 ; however, the structural basis for RAF regulation is poorly understood at present. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to determine autoinhibited and active-state structures of full-length BRAF in complexes with MEK1 and a 14-3-3 dimer. The reconstruction reveals an inactive BRAF-MEK1 complex restrained in a cradle formed by the 14-3-3 dimer, which binds the phosphorylated S365 and S729 sites that flank the BRAF kinase domain. The BRAF cysteine-rich domain occupies a central position that stabilizes this assembly, but the adjacent RAS-binding domain is poorly ordered and peripheral. The 14-3-3 cradle maintains autoinhibition by sequestering the membrane-binding cysteine-rich domain and blocking dimerization of the BRAF kinase domain. In the active state, these inhibitory interactions are released and a single 14-3-3 dimer rearranges to bridge the C-terminal pS729 binding sites of two BRAFs, which drives the formation of an active, back-to-back BRAF dimer. Our structural snapshots provide a foundation for understanding normal RAF regulation and its mutational disruption in cancer and developmental syndromes.
- Department of Cancer Biology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: