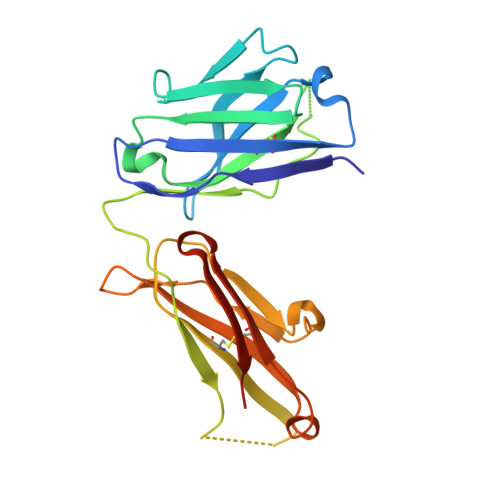
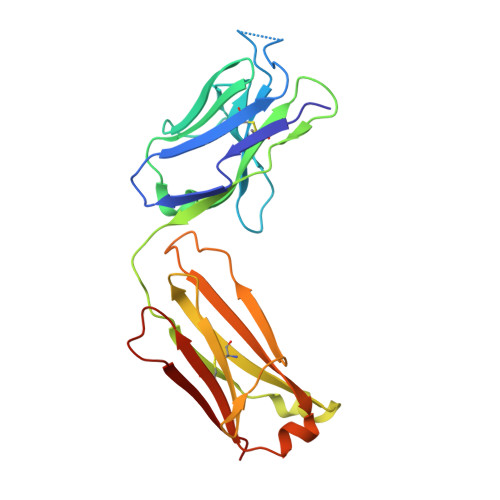
Rapid and robust antibody Fab fragment crystallization utilizing edge-to-edge beta-sheet packing.
Lieu, R., Antonysamy, S., Druzina, Z., Ho, C., Kang, N.R., Pustilnik, A., Wang, J., Atwell, S.(2020) PLoS One 15: e0232311-e0232311
- PubMed: 32915778
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232311
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WG8, 6WGB, 6WGJ, 6WGK, 6WGL, 6WIO, 6WIR - PubMed Abstract:
Antibody therapeutics are one of the most important classes of drugs. Antibody structures have become an integral part of predicting the behavior of potential therapeutics, either directly or as the basis of modeling. Structures of Fab:antigen complexes have even greater value. While the crystallization and structure determination of Fabs is easy relative to many other protein classes, especially membrane proteins, broad screening and optimization of crystalline hits is still necessary. Through a comprehensive review of rabbit Fab crystal contacts and their incompatibility with human Fabs, we identified a small secondary structural element from the rabbit light chain constant domain potentially responsible for hindering the crystallization of human Fabs. Upon replacing the human kappa constant domain FG loop (HQGLSSP) with the two residue shorter rabbit loop (QGTTS), we dramatically improved the crystallization of human Fabs and Fab:antigen complexes. Our design, which we call "Crystal Kappa", enables rapid crystallization of human fabs and fab complexes in a broad range of conditions, with less material in smaller screens or from dilute solutions.
- Biotechnology Discovery Research, Applied Molecular Evolution, Eli Lilly and Company, San Diego, CA, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: