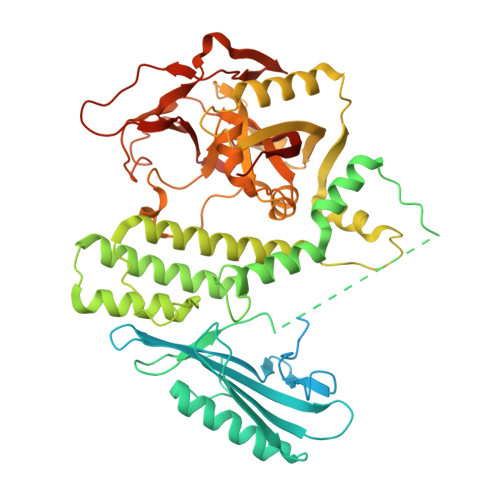
Bridging of DNA breaks activates PARP2-HPF1 to modify chromatin.
Bilokapic, S., Suskiewicz, M.J., Ahel, I., Halic, M.(2020) Nature 585: 609-613
- PubMed: 32939087
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2725-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WZ5, 6WZ9, 6X0L, 6X0M, 6X0N - PubMed Abstract:
Breaks in DNA strands recruit the protein PARP1 and its paralogue PARP2 to modify histones and other substrates through the addition of mono- and poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) 1-5 . In the DNA damage responses, this post-translational modification occurs predominantly on serine residues 6-8 and requires HPF1, an accessory factor that switches the amino acid specificity of PARP1 and PARP2 from aspartate or glutamate to serine 9,10 . Poly(ADP) ribosylation (PARylation) is important for subsequent chromatin decompaction and provides an anchor for the recruitment of downstream signalling and repair factors to the sites of DNA breaks 2,11 . Here, to understand the molecular mechanism by which PARP enzymes recognize DNA breaks within chromatin, we determined the cryo-electron-microscopic structure of human PARP2-HPF1 bound to a nucleosome. This showed that PARP2-HPF1 bridges two nucleosomes, with the broken DNA aligned in a position suitable for ligation, revealing the initial step in the repair of double-strand DNA breaks. The bridging induces structural changes in PARP2 that signal the recognition of a DNA break to the catalytic domain, which licenses HPF1 binding and PARP2 activation. Our data suggest that active PARP2 cycles through different conformational states to exchange NAD + and substrate, which may enable PARP enzymes to act processively while bound to chromatin. The processes of PARP activation and the PARP catalytic cycle we describe can explain mechanisms of resistance to PARP inhibitors and will aid the development of better inhibitors as cancer treatments 12-16 .
- Department of Structural Biology, St Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, TN, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: