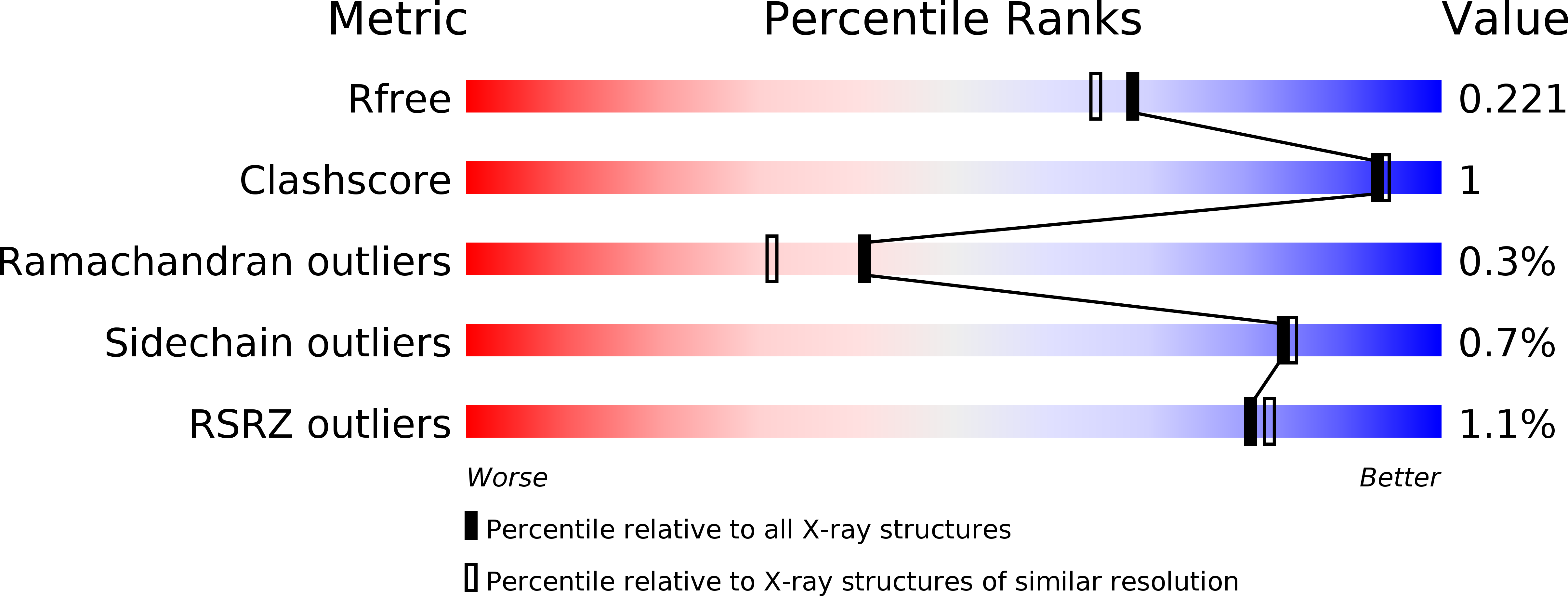
Two Methods, One Goal: Structural Differences between Cocrystallization and Crystal Soaking to Discover Ligand Binding Poses.
Wienen-Schmidt, B., Oebbeke, M., Ngo, K., Heine, A., Klebe, G.(2021) ChemMedChem 16: 292-300
- PubMed: 33029876
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202000565
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6YNA, 6YNB, 6YNC, 6YNR, 6YNT, 6YQI, 6YQJ, 6YQK - PubMed Abstract:
In lead optimization, protein crystallography is an indispensable tool to analyze drug binding. Binding modes and non-covalent interaction inventories are essential to design follow-up synthesis candidates. Two protocols are commonly applied to produce protein-ligand complexes: cocrystallization and soaking. Because of its time and cost effectiveness, soaking is the more popular method. Taking eight ligand hinge binders of protein kinase A, we demonstrate that cocrystallization is superior. Particularly for flexible proteins, such as kinases, and larger ligands cocrystallization captures more reliable the correct binding pose and induced protein adaptations. The geometrical discrepancies between soaking and cocrystallization appear smaller for fragment-sized ligands. For larger flexible ligands that trigger conformational changes of the protein, soaking can be misleading and underestimates the number of possible polar interactions due to inadequate, highly impaired positions of protein amino-acid side and main chain atoms. Thus, if applicable cocrystallization should be the gold standard to study protein-ligand complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Pharmazeutische Chemie, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Marbacher Weg 6, 35032, Marburg, Germany.