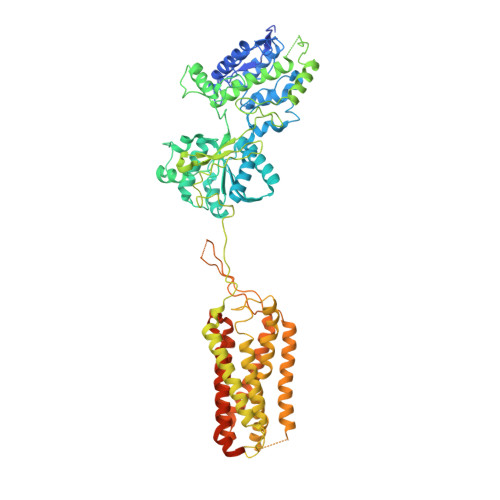
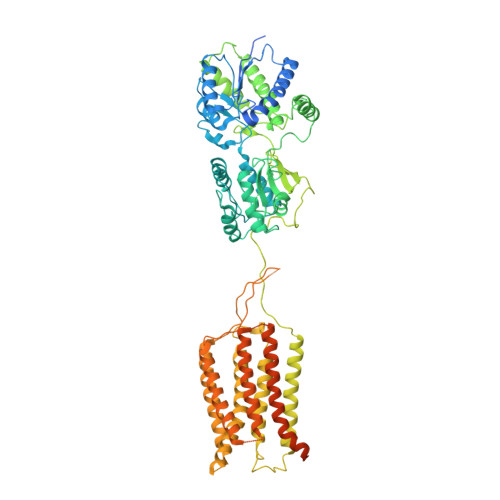
Structural Basis for Activation of the Heterodimeric GABA B Receptor.
Kim, Y., Jeong, E., Jeong, J.H., Kim, Y., Cho, Y.(2020) J Mol Biology 432: 5966-5984
- PubMed: 33058878
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.09.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CA3, 7CA5, 7CUM - PubMed Abstract:
The neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activates the metabotropic GABA B receptor to generate slow, prolonged inhibitory signals that regulate the neural circuitry. The GABA B receptor is an obligate heterodimeric G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) comprised of GBR1 and GBR2 subunits, each with extracellular, seven-helix transmembrane (7TM), and coiled-coil domains. To understand how GABA-driven conformational changes in the extracellular domain are transmitted to the 7TM domain during signal transduction, we determined cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of GABA B in two different states: an antagonist-bound inactive state, and an active state in which both the GABA agonist and a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) are bound. In the inactive state, the TM3 and TM5 helices in the two 7TM domains engage in cholesterol-mediated as well as direct interactions, resulting in an open conformation. GABA binding forces the extracellular domains of GBR1 and GBR2 into a compact form, relocating the linkers that connect the extracellular and 7TM domains closer to each other. The movement of the linker along with the associated extracellular loop 2 of the 7TM domain reorients the two 7TM domains and creates a new interface with the TM5, TM6 and TM7 helices in a closed conformation. PAM binding to the interface between the TM6 and TM6 helices stabilizes the active 7TM domain conformation. The relayed structural rearrangement results in significant conformational changes in the TM helices, as well as intracellular loop 3 in GBR2, which may promote the binding and activation of the Gi/o proteins.
- Department of Life Science, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Pohang, Republic of Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: