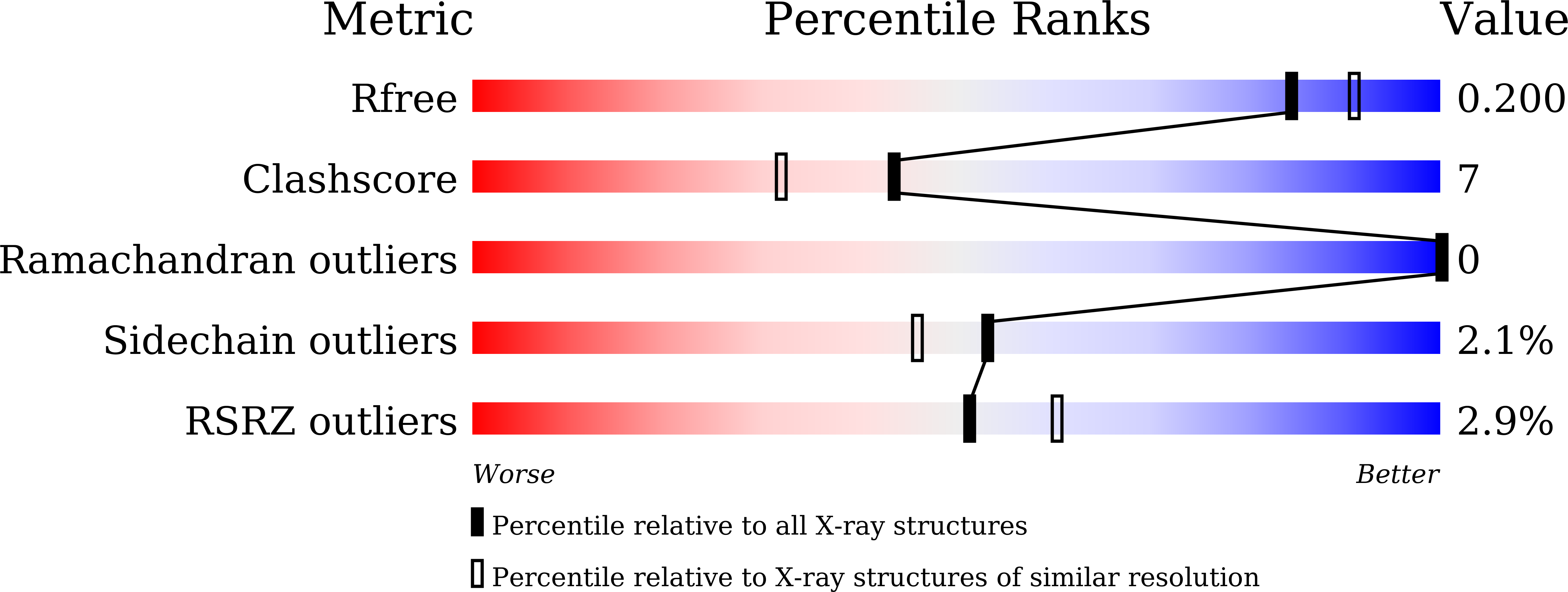
Crystal structures of gamma-glutamylmethylamide synthetase provide insight into bacterial metabolism of oceanic monomethylamine.
Wang, N., Chen, X.L., Gao, C., Peng, M., Wang, P., Zhang, N., Li, F., Yang, G.P., Shen, Q.T., Li, S., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y.Z., Li, C.Y.(2020) J Biol Chem 296: 100081-100081
- PubMed: 33199371
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015952
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7CQL, 7CQN, 7CQQ, 7CQU, 7CQW, 7CQX - PubMed Abstract:
Monomethylamine (MMA) is an important climate-active oceanic trace gas and ubiquitous in the oceans. γ-Glutamylmethylamide synthetase (GmaS) catalyzes the conversion of MMA to γ-glutamylmethylamide, the first step in MMA metabolism in many marine bacteria. The gmaS gene occurs in ∼23% of microbial genomes in the surface ocean and is a validated biomarker to detect MMA-utilizing bacteria. However, the catalytic mechanism of GmaS has not been studied because of the lack of structural information. Here, the GmaS from Rhodovulum sp. 12E13 (RhGmaS) was characterized, and the crystal structures of apo-RhGmaS and RhGmaS with different ligands in five states were solved. Based on structural and biochemical analyses, the catalytic mechanism of RhGmaS was explained. ATP is first bound in RhGmaS, leading to a conformational change of a flexible loop (Lys287-Ile305), which is essential for the subsequent binding of glutamate. During the catalysis of RhGmaS, the residue Arg312 participates in polarizing the γ-phosphate of ATP and in stabilizing the γ-glutamyl phosphate intermediate; Asp177 is responsible for the deprotonation of MMA, assisting the attack of MMA on γ-glutamyl phosphate to produce a tetrahedral intermediate; and Glu186 acts as a catalytic base to abstract a proton from the tetrahedral intermediate to finally generate glutamylmethylamide. Sequence analysis suggested that the catalytic mechanism of RhGmaS proposed in this study has universal significance in bacteria containing GmaS. Our results provide novel insights into MMA metabolism, contributing to a better understanding of MMA catabolism in global carbon and nitrogen cycles.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Marine Biotechnology Research Center, Shandong University, Qingdao, China; College of Marine Life Sciences, and Frontiers Science Center for Deep Ocean Multispheres and Earth System, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China.