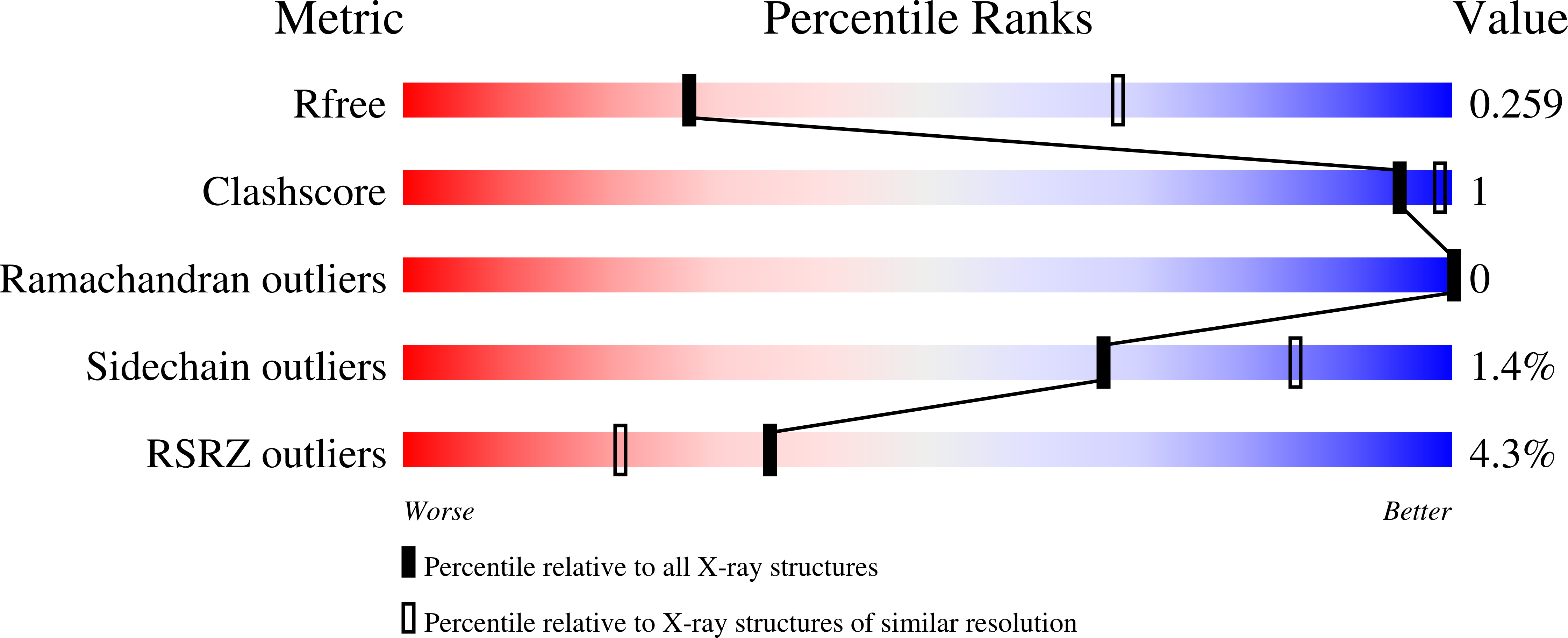
Simultaneous binding of Guidance Cues NET1 and RGM blocks extracellular NEO1 signaling.
Robinson, R.A., Griffiths, S.C., van de Haar, L.L., Malinauskas, T., van Battum, E.Y., Zelina, P., Schwab, R.A., Karia, D., Malinauskaite, L., Brignani, S., van den Munkhof, M.H., Dudukcu, O., De Ruiter, A.A., Van den Heuvel, D.M.A., Bishop, B., Elegheert, J., Aricescu, A.R., Pasterkamp, R.J., Siebold, C.(2021) Cell 184: 2103
- PubMed: 33740419
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.045
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NDG, 7NE0, 7NE1 - PubMed Abstract:
During cell migration or differentiation, cell surface receptors are simultaneously exposed to different ligands. However, it is often unclear how these extracellular signals are integrated. Neogenin (NEO1) acts as an attractive guidance receptor when the Netrin-1 (NET1) ligand binds, but it mediates repulsion via repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) ligands. Here, we show that signal integration occurs through the formation of a ternary NEO1-NET1-RGM complex, which triggers reciprocal silencing of downstream signaling. Our NEO1-NET1-RGM structures reveal a "trimer-of-trimers" super-assembly, which exists in the cell membrane. Super-assembly formation results in inhibition of RGMA-NEO1-mediated growth cone collapse and RGMA- or NET1-NEO1-mediated neuron migration, by preventing formation of signaling-compatible RGM-NEO1 complexes and NET1-induced NEO1 ectodomain clustering. These results illustrate how simultaneous binding of ligands with opposing functions, to a single receptor, does not lead to competition for binding, but to formation of a super-complex that diminishes their functional outputs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford OX3 7BN, UK.